Thermistor or Thermal Resistor is a two terminal semiconductor device whose resistance is a temperature sensitive.
Working Principle of Thermistor
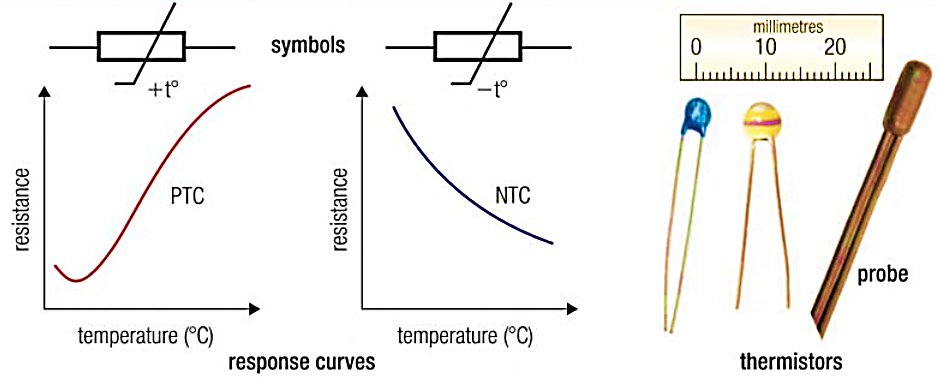
Thermistor have a Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) i.e. resistance decreases as the temperature increases. The materials used in the manufacture of thermistors include oxides of cobalt, nickel, copper, iron, uranium and manganese. The thermistor has very high temperature coefficient of resistance of the order of 3 to 5% per ºC. The resistance at any temperature T is given by,
\[{{R}_{T}}={{R}_{0}}\text{ exp }\beta \text{ }\left( \frac{1}{T}-\frac{1}{{{T}_{0}}} \right)\]
Where,
RT – Thermistor resistance at temperature T (K)
R0 – Thermistor resistance at temperature T0 (K)
β – A constant determined by calibration
At high temperature, equation (1) reduces to,
\[{{R}_{T}}={{R}_{0}}\text{ exp }\left( \frac{\beta }{T} \right)\]
Working & Symbol of Thermistor
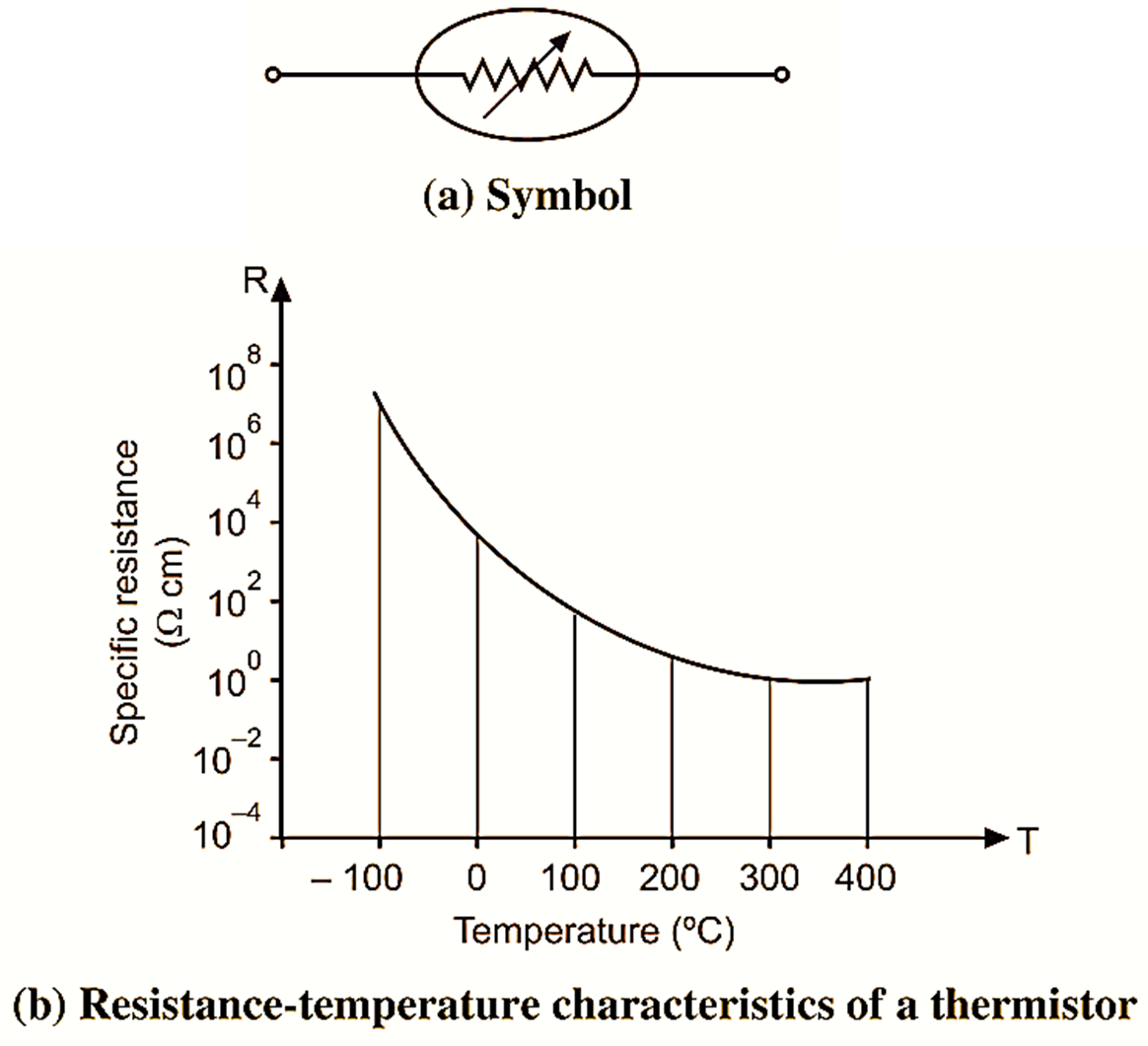
Figure 1.
The resistance-temperature characteristics is shown in Fig. 1 (b) and symbol in Fig. 1 (a). The curve is non-linear and the drop in resistance from 500Ω to 100Ω occurs for an increase in temperatures from 20 to 100ºC. The temperature of the device can be changed internally or externally. An increase in current through the device will raise its temperature carrying a drop in its terminal resistance. Any externally applied heat source will result in an increase in its body temperature and drop in resistance. This action tends itself well to control mechanisms.
Types of Thermistor
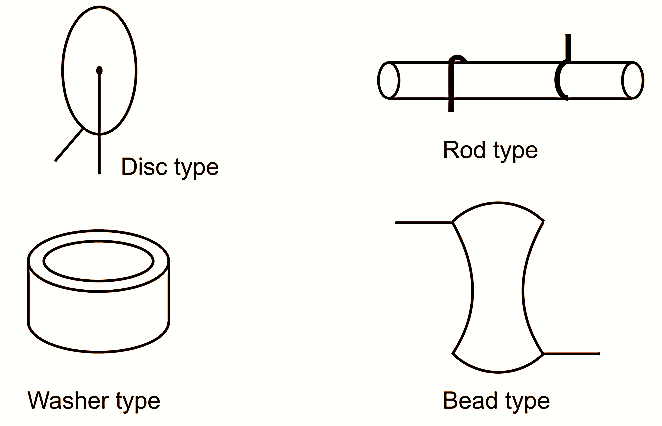
Figure 2: Various configurations of thermistor.
The thermistors are available in various configurations such as beads, disc, rod, washer as shown in Fig. 2. The smallest thermistors are made in the form of beads. Some are as small as 0.15 mm in diameter. And where greater power dissipation is required, thermistors obtained are in disc, washer or rod forms.
Advantages of Thermistor
- Small size and low cost.
- Fast response over narrow temperature range.
- Good sensitivity in the NTC region.
Disadvantages of Thermistor
- Non-linearity in resistance versus temperature characteristics.
- Unsuitable for wide temperature range.
- Very low excitation current to avoid self-heating.
- Need of shielded power lines, filters etc. due to high resistance.