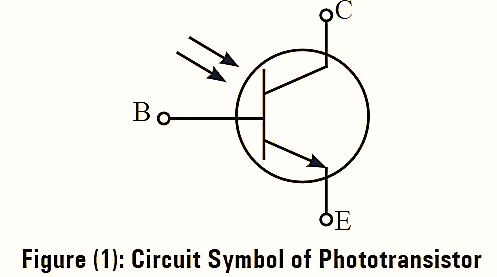
The phototransistor is an optoelectronic device that generates or detects the signals from light incident on it. The symbol of phototransistor is shown in figure (1).
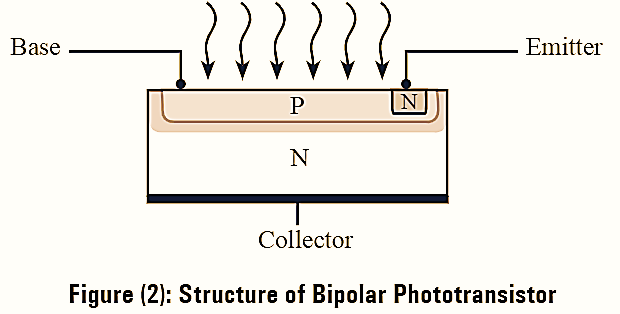
The structure of a NPN bipolar phototransistor is illustrated in figure (2). The phototransistor is basically operated in an open-base configuration.
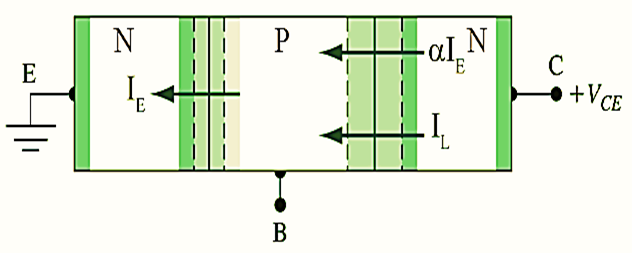
Figure 3: Diagram of an open-base phototransistor.
The schematic representation of open-base phototransistors is depicted in figure (3). From figure (3), it can be observed that the width of depletion region or junction between base and collector is large. When the base-collector junction is in reverse bias, the charge carriers emit out of the region and generates a photocurrent, IL If the base-emitter junction is forward biased, the photo-transistor operates as a basic semiconductor BJT. From figure (3), the total current coming out from the emitter terminal is given by,
\[{{I}_{E}}=\alpha {{I}_{E}}+{{I}_{L}}\]
Here,
α – Current gain CB configuration.
As the base is open-circuited IB = 0, which implies,
\[{{I}_{E}}={{I}_{C}}\] \[{{I}_{C}}=\alpha {{I}_{C}}+{{I}_{L}}\]
\[{{I}_{C}}(1-\alpha )={{I}_{L}}\] \[{{I}_{C}}=\frac{{{I}_{L}}}{1-\alpha }\]
Since,
\[\beta =\frac{\alpha }{1-\alpha }\text{ and }\alpha =\frac{\beta }{1+\beta }\]
\[\frac{\beta }{\alpha }=1+\beta \]
\[1+\beta =\frac{1}{1-\alpha }\]
\[{{I}_{C}}=(1+\beta ){{I}_{L}}\]
The factor (l + β) indicates the amount of amplification of IL in a phototransistor. The frequency response of a phototransistor having a large Base-Collector junction area is limited by a capacitor. It can also be reduced using the Miller effect.
Applications of Phototransistor
- In optocouplers, it is used as light detector.
- It is used in punch card readers.
- In digital logic circuits.
- It is used in traffic light controllers, level indication devices, etc.
- In SCR triggering circuits at low light levels.