A single phase non-salient pole synchronous motor with no D.C excitation is known as hysteresis motor. This motor is so called because it runs on torque produced by the hysteresis loss induced in the rotor.
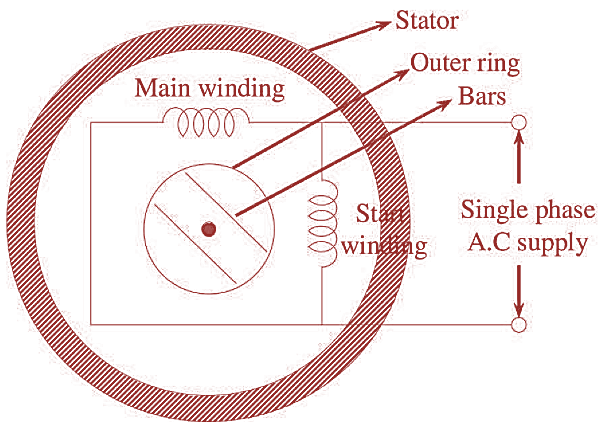
Figure 1: Hysteresis Motor.
Construction of Hysteresis Motor
The stator of this motor has two windings which are connected to a single phase A.C supply at both the starting and running period of the motor. As a result, a rotating magnetic field is produced by phase splitting principle due to which hysteresis losses are induced in the rotor.
The rotor used in this motor is cylindrical (non-salient) type which is usually made of hardened and high retentivity steel. It consists of outer ring and cross bars as shown in figure (1).
Working of Hysteresis Motor
When the motor is fed by single phase A.C supply, a rotating magnetic field is produced. Due to this magnetic field eddy currents are induced in the steel of rotor which move across the two bars path. As the rotor is made of high retentivity material a large amount of hysteresis losses take place and suitable amount of energy is required in reversing the current direction of rotor. The rotor magnetic field setup by eddy current allows the rotor to rotate. The starting torque is high because of high hysteresis loss. When motor reaches the synchronous speed, rotor bars are permanently magnetized in one direction and continuously rotate at synchronous speed. Hence its accelerating torque is always constant.
Mechanical power developed by rotor is given as,
\[{{P}_{m}}={{P}_{h}}\left( \frac{1-s}{s} \right)\] Where,
Ph is hysteresis loss.
Hysteresis torque is given by,
\[{{T}_{h}}=\frac{9.55{{P}_{m}}}{{{N}_{s}}}\]
Figure (2) shows the torque-speed characteristics of hysteresis motor.
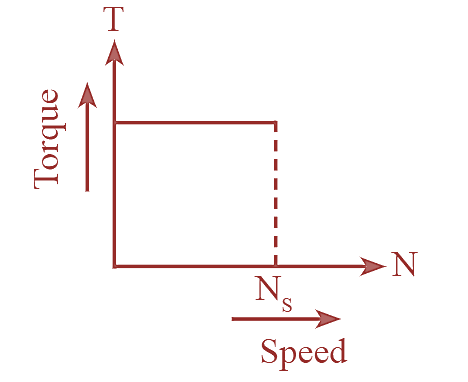
Figure 1: Torque-Speed characteristics of Hysteresis Motor.
Advantages of Hysteresis Motor
- It does not produce any mechanical vibrations due to the absence of rotor teeth and winding.
- Its operation is very silent (no noise).
- Its accelerating torque is always constant.
- It can operate at multispeed by using gear trains.
- It is suitable for high inertia loads.
Applications of Hysteresis Motor
Due to the noiseless operation, these motors are used in sound recording instruments, sound producing equipments, electric clocks, tape printers, tape recorders, indicating devices etc.