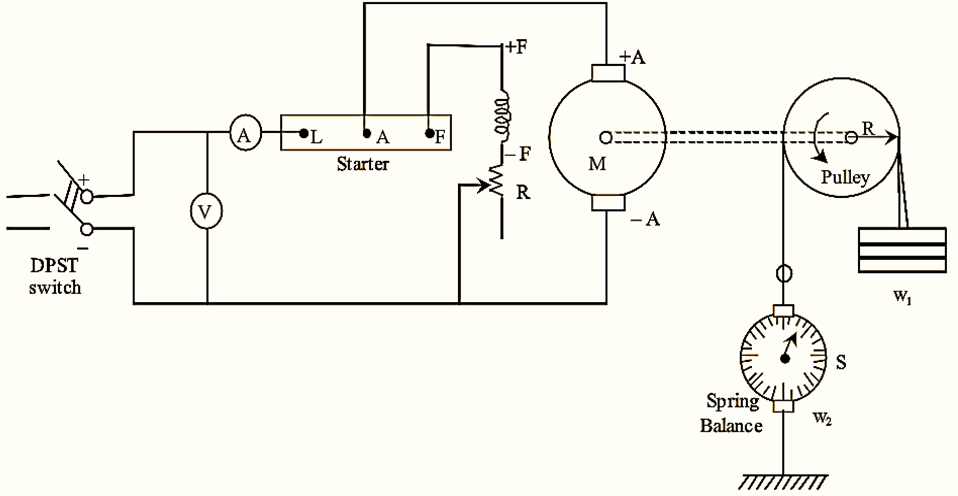
Figure 1: Arrangement of Brake Test.
Brake test is a direct testing method used to find the efficiency of a DC motor. The arrangement for performing brake test on a DC motor is shown in figure (1). In this test, brakes are applied on a water cooled pulley mounted on the motor shaft depending upon the rating of the machine. The brake rope is fixed with the help of wooden blocks gripping the pulley. One end of the rope is fixed to the earth via spring balance ‘B’ and the other end is connected to a suspended weight ‘W1‘. Now, the motor is allowed to run under this condition and the load on the motor is so adjusted that it carries full-load current by adding or removing the weights to suspended weight ‘W1’ Let reading on spring balance ‘B’ be ‘W2‘.
While increasing the load, the load is increased in step by step manner until full-load condition is achieved and for each step various values of voltmeter, ammeter, the suspension weights i.e., W1 and W2 and speed of the motor are noted and the efficiency of the rotor can be calculated as follows,
The net pull on the rope due to friction at the pulley is given as,
\[=({{W}_{1}}-{{W}_{2}})\text{ kg wt}\]
\[\text{= 9}\text{.81 (}{{W}_{1}}-{{W}_{2}}\text{) Newton}\]
The shaft torque Tsh developed by the motor is given by,
\[{{\text{T}}_{sh}}=({{W}_{1}}-{{W}_{2}})\text{ R kg-mt}\]
\[\text{= 9}\text{.81 }({{W}_{1}}-{{W}_{2}})\text{ R N-m}\]
Where,
R = Radius of pulley (mts)
Motor power output is given by,
\[{{P}_{out}}={{T}_{sh}}\times \omega \text{ watts}\]
\[\text{=}\frac{2\pi \times 9.81}{60}({{W}_{1}}-{{W}_{2}})\text{ RN watts}\]
\[\text{= 1}\text{.027 N }({{W}_{1}}-{{W}_{2}})\text{ R watts}\]
Where,
Let,
V = Supply voltage
I = Full-load current taken by the motor.
Input power is given is,
\[{{\text{P}}_{in}}=VI\text{ watts}\]
The efficiency is given by,
\[%\eta =\frac{\text{Output power}}{\text{Input power}}\times 100\]
\[=\frac{\frac{2\pi \times 9.81}{60}({{W}_{1}}-{{W}_{2}})\text{ RN}}{VI}\times 100\]
\[=\frac{1.027({{W}_{1}}-{{W}_{2}})\text{ RN}}{VI}\times 100\]
Advantages of Brake Test
- Test requires no other machines. Hence, it reduces the cost and energy.
- This method is very simple.
- Very much convenient for small motors.
Disadvantages of Brake Test
- This test is performed with only small motors. In case of large motors it is difficult to dissipate the large amount of heat generated at the brake.
- The output of the motor cannot be determined accurately because of the unavoidable errors occurring in spring balance which leads to incorrect determination of the internal losses or efficiency of a DC machine.
- In case of series wound machines care should be taken so that the brake applied is tight otherwise the motor will attain dangerously high speed, which leads to severe damage.