A solar cell or photovoltaic cell is a semiconductor PN junction device with no direct supply across the junction. It transforms the light or photon energy incident on it into electrical power and delivers to the load.
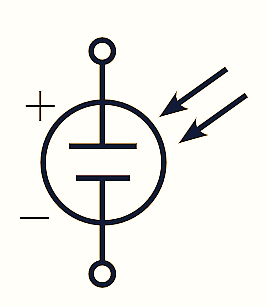
Figure 1: Solar Cell Symbol.
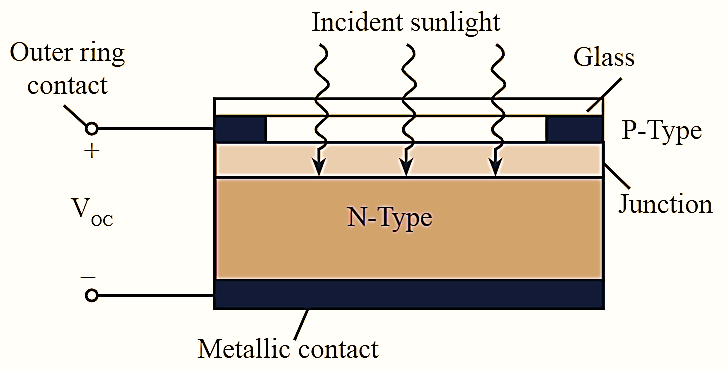
The symbol (see Figure 1) and basic structure (see Figure 2) of a silicon PN junction solar cell are illustrated in figure (1). The solar cells are designed in such a way that the surface area must be normal to incident light. A P-Type material of thickness sufficient to allow maximum photons to reach the junction is connected to a metallic conductor. In this region, the photon provides specific amount of energy to valance electrons, so that the electrons leave parent atom and results in number of free electrons and holes. In P-type and N-type materials, the minority charge carriers i.e., electrons and holes respectively that are produced by incident photon moves freely across the junction. The above process leads to increase in minority carrier flow that is opposite to the direction of forward current of PN junction. Hence, the photo current in the device increases in reverse biased condition. When the diode is forward biased, the electric field at the junction decreases, but the direction of current flow does not change. Since, in photo cell, the net current is due to the photo cun•ent in reverse direction, it is expressed as,
\[I={{I}_{L}}-{{I}_{F}}\]
Here,
IL — Photo current
IF — Forward current
\[{{I}_{F}}={{I}_{S}}\left[ {{e}^{\left( \frac{qv}{kt} \right)}}-1 \right]\]
\[I={{I}_{L}}-{{I}_{S}}\left[ {{e}^{\left( \frac{qv}{kt} \right)}}-1 \right]\]
V-I Characteristics of Solar Cell
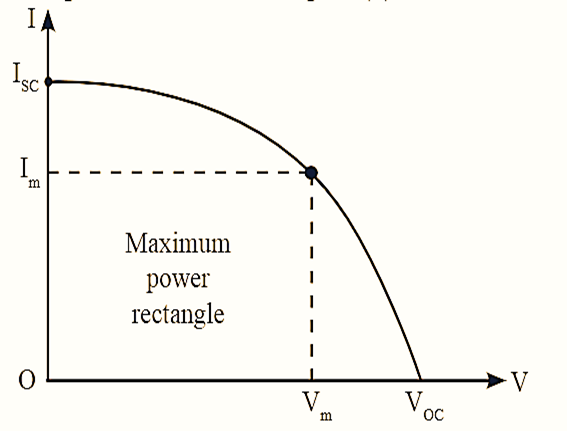
Figure 3: V-I Characteristics of Solar Cell.
The V-I characteristics of solar cell is plotted as shown in figure (3). From figure (3), it can be observed that, under short-circuit condition i.e., for V = 0, the intersection point on vertical axis indicates short circuit current, ISC. In this case the resistance of the device and the current is zero and ISC the i.e,
\[I={{I}_{SC}}={{I}_{L}}\]
If the resistance of the device increases to infinite value i.e., R tends to ∞, the net current in solar cell is zero and voltage is open-circuit voltage, Voc Hence, equation (1) can be rewritten as,
\[I={{I}_{L}}-{{I}_{S}}\left[ {{e}^{\left( \frac{qV}{kT} \right)-1}} \right]\]
\[0={{I}_{L}}-{{I}_{S}}\left[ {{e}^{\left( \frac{qV}{kT} \right)-1}} \right]\]
\[{{I}_{L}}={{I}_{S}}\left[ {{e}^{\left( \frac{qV}{kT} \right)-1}} \right]\]
\[1+\frac{{{I}_{L}}}{{{I}_{S}}}={{e}^{\left( \frac{qV}{kT} \right)-1}}\]
\[{{V}_{oc}}=\frac{kT}{q}\text{lo}{{\text{g}}_{e}}\left[ 1+\frac{{{I}_{L}}}{{{I}_{S}}} \right]\]
Here,
Is — Saturation current
\[{{V}_{oc}}=\eta {{V}_{T}}{{\log }_{e}}\left[ 1+\frac{{{I}_{L}}}{{{I}_{S}}} \right]\]
Where,
η = 1 for Ge and 2 for Si,
Solar cells are widely used in space vehicles, calculators, satellites and so on.
Advantages of Solar Cells
The following are the some of advantages of solar cell.
- Operating cost is very less
- It is more reliable device
- It is easy to install
- It can be operated at ambient temperature ranges
- Fuel source is vast and essentially infinite (eg: Sun light)
Disadvantages of Solar Cells
The following are the disadvantages of solar cell.
- The density of source i.e., light is very low
- Installation cost is very high
- Energy i.e., electricity can be generated only during day time.