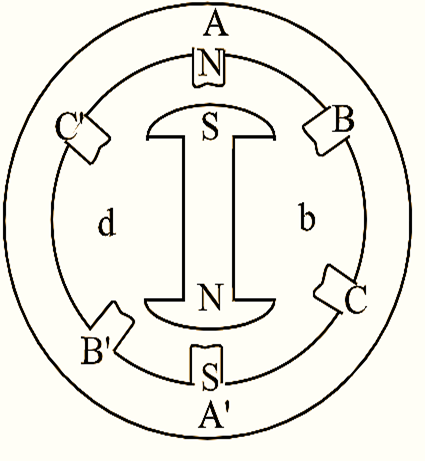
Figure 1: Permanent Magnet Stepper Motor.
Construction of Permanent Magnet Stepper Motor
The stator of the Permanent Magnet Stepper Motor is similar to that of the variable reluctance stepper motor, whereas the rotor is replaced by a permanent magnet. In this type of stepper motor the stepping angle would be more due to difficulty in manufacturing the rotor with number of poles. The basic structure of a two pole motor is as shown in figure 1.
Working of Permanent Magnet Stepper Motor
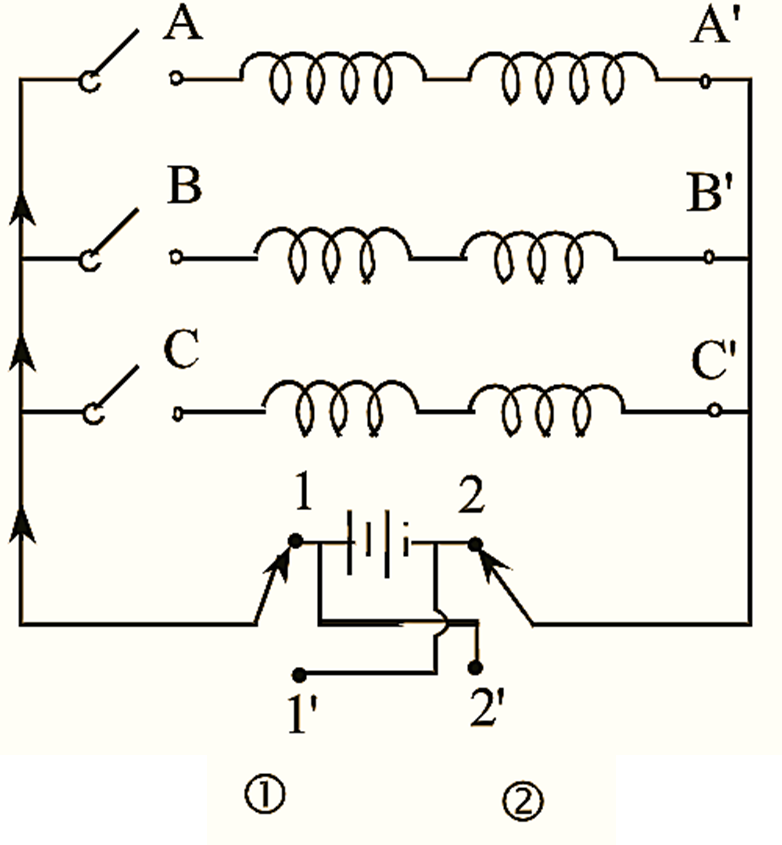
In the equivalent circuit shown with supply source connected (see Figure 2), the current flows in the forward direction, when phase A is energized with A-north and A’-south the position of rotor is as shown in the figure. When phase B is energized with B-north and B’-south the rotor rotates in clockwise direction with an angular shift of β i.e., 60º and again it moves 60º when C phase is energized. After the rotation of 120º, if again phase A is fed supply, then the rotor moves in the anticlockwise direction due to the repulsive force between the like poles.
In order to keep the rotation in same direction, it is required to change the polarity either by interchanging the winding coil terminals or by changing the supply source. The circuit shows the method of changing the source terminals. This change in current should be done after every k angle of rotation.
\[k=\frac{360{}^\circ }{\text{Number of phases}}\]
This motor is also called as variable speed brushless D.C motor.