A lead-acid battery is a type of rechargeable battery commonly used in vehicles, renewable energy systems, and backup power applications. It is known for its reliability and affordability.
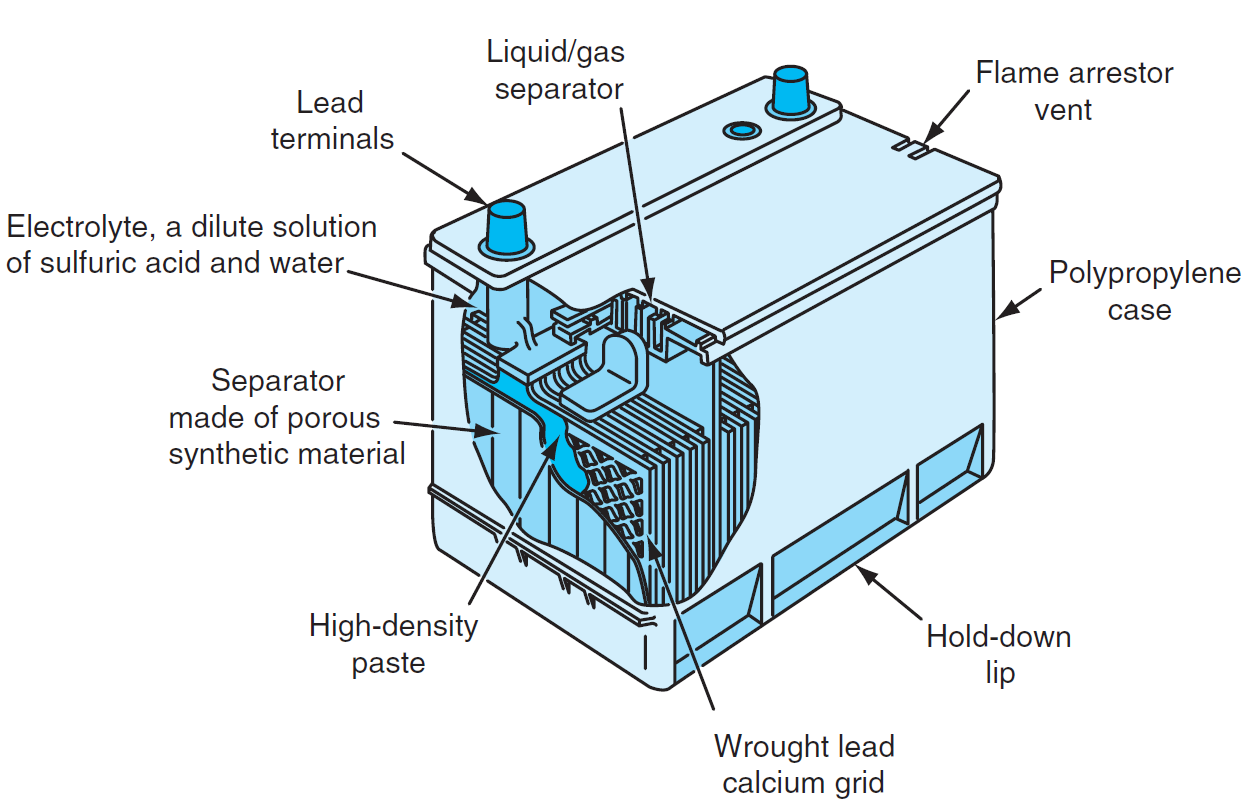
Parts of Lead Acid Battery
- Electrolyte: A dilute solution of sulfuric acid and water, which facilitates the electrochemical reactions.
- Positive Plate: Made of lead dioxide (PbO₂), it serves as the cathode.
- Negative Plate: Made of sponge lead (Pb), it serves as the anode.
- Separators: Porous synthetic materials that prevent physical contact between the positive and negative plates while allowing ionic flow.
- Grid: Wrought lead-calcium alloy grids provide structural support and conduct electricity.
- High-Density Paste: Active material applied to the plates to enhance chemical reactions.
- Case: Made of polypropylene to protect internal components and contain the electrolyte.
- Vents/Flame Arrestor: Allows gas release while preventing external sparks or flames from igniting hydrogen gas.
- Terminals: Connect the battery to the external circuit.
Working Principle of Lead Acid Battery
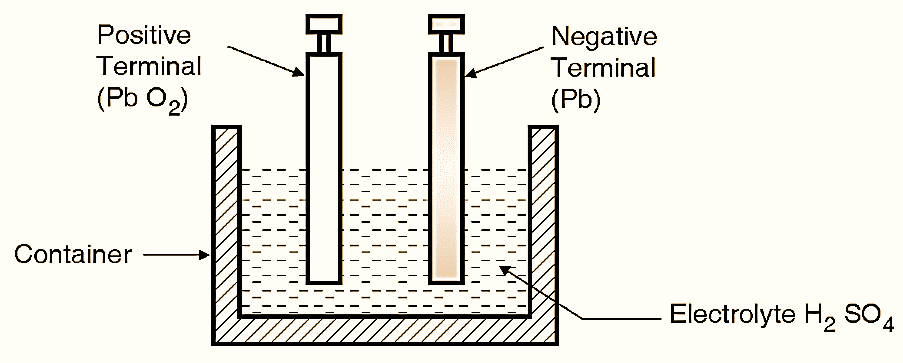
Figure 1: Lead Acid Battery.
The battery cells in which the chemical action taking place is reversible are known as the lead acid battery cells. So it is possible to recharge a lead acid battery cell if it is in the discharged state.
In the charging process we have to pass a charging current through the cell in the opposite direction to that of the discharging current. The electrical energy is stored in the form of chemical form, when the charging current is passed, lead acid battery cells are capable of producing a large amount of energy.
Construction of Lead Acid Battery
The construction of a lead acid battery cell is as shown in Fig. 1. It consists of the following parts :
- Anode or positive terminal (or plate).
- Cathode or negative terminal (or plate).
- Electrolyte.
- Separators.
Anode or positive terminal (or plate):
The positive plates are also called as anode. The material used for it is lead peroxide (PbO2). It is a material of dark brown colour.
Cathode or negative terminal (or plate):
The negative plates are also called as cathode. The material used for the cathode is lead (Pb) and its colour is gray.
Electrolyte :
The electrolyte used is dilute sulphuric acid (H2SO4) with 3-parts of distilled water mixed with one part of H2SO4. The specific gravity is 1.2. The anode and cathode both are immersed in the electrolyte.
Separators :
These are thin plates of porous insulated material like rubber. They are placed between main plates to avoid short circuit between the positive and negative plates.
The main plates are placed close to each other to reduce the internal resistance.
Container :
The container is made up of plastic or ceramic or rubber. All plates and electrolyte is placed in it. No chemical action should take place on the container.
Working of a Lead Acid Battery
Discharging action of the cell :
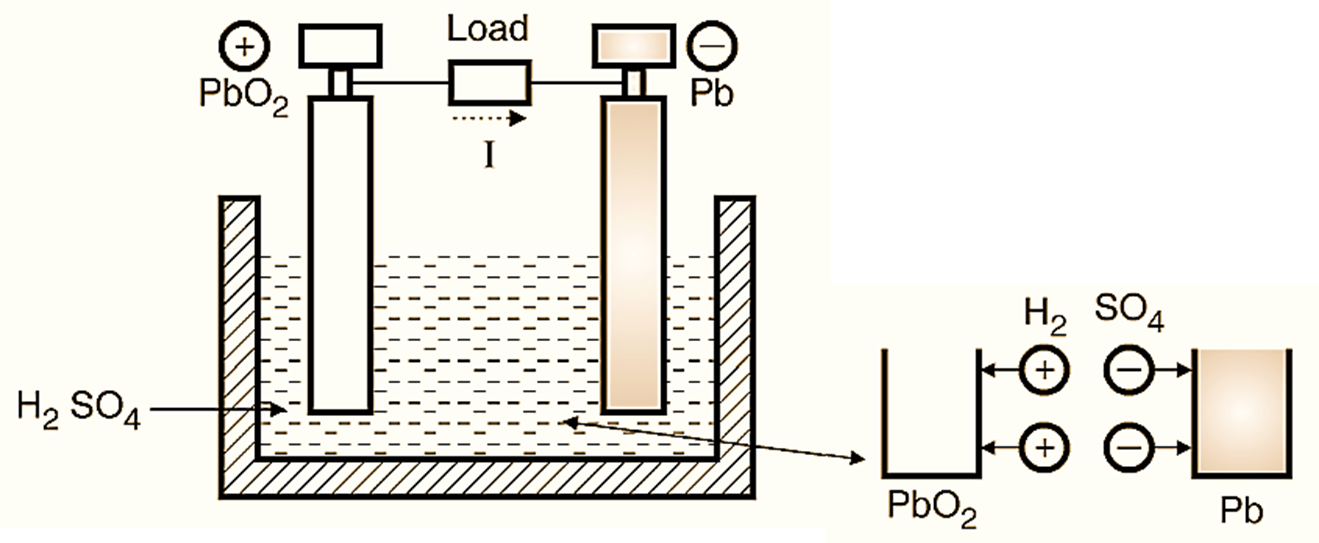
Figure 2: Discharging of Lead Acid Battery.
Assume that the cell is fully charged. When it starts discharging, the current starts flowing from the cell to the external load as shown in Fig. 2. Due to this current, the sulphuric acid H2SO4 is disassociated into positive H2 and negative SO4 Ions. The external load current flows from anode to cathode, but the internal current flows from cathode to anode through the electrolyte. Therefore the positive H2 ions move to the anode and the negative SO4 ions move to the cathode. The chemical action during Discharge is as follows :
At Anode :
\[\text{Pb}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ + }{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ + }{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\to \text{ PbS}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\text{ + 2 }{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\]
At Cathode :
\[\text{ Pb + S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\to \text{ PbS}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\]
Both the above expressions show that both the electrodes, anode and cathode become PbSO4 (see RHS of Equations and water (H2O) is also produced. Due to formation of PbSO4, both the electrodes become whitish and due to the water formation, the specific gravity of the electrolyte reduces. Hence the output voltage of the cell decreases on discharging.
Charging action of the cell :
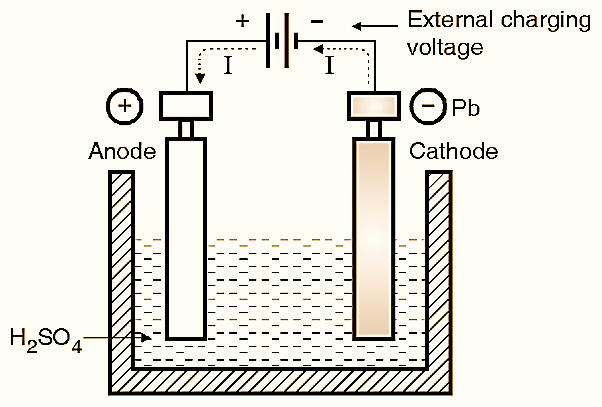
Figure 3: Charging of Lead Acid Battery.
As we have already explained, when the cell is completely discharged, the anode and cathode both transform into PbSO4 (which is whitish in colour). During the charging process, a positive external voltage is applied to the anode of the battery and negative voltage is applied at the cathode as shown in Fig. 3. Due to the externally connected source, the current flows from anode to cathode inside the electrolyte. This current results in the following chemical action.
At Anode :
\[\text{ PbS}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}+\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\text{ +2}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O }\to \text{ Pb}{{\text{O}}_{2}}+2{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\]
At Cathode :
\[\text{ PbS}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}+{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\to {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\]
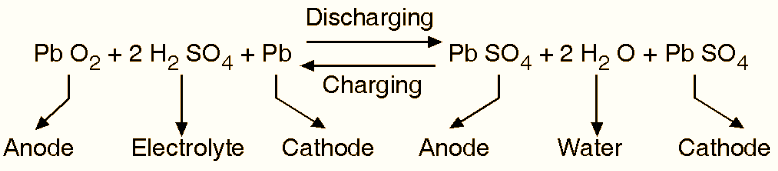
These two expressions indicate (see RHS) that “PbO2” is being formed at the anode and “Pb” at the cathode. Along with that the sulphuric acid (H2SO4) is being created newly. As the water is consumed and H2SO4 is created, the specific gravity of H2SO4 increases, energy is absorbed and the voltage on the cell increases, and the charging is said to have taken place. The single reversible equation representing the charging and discharging process is given by,
Advantages of a Lead Acid Battery
- Low Cost: Relatively inexpensive compared to other rechargeable batteries.
- Reliable: Proven technology with consistent performance over decades.
- High Surge Current: Suitable for applications requiring high starting power (e.g., in vehicles).
- Recyclable: High recyclability of lead and other components, reducing environmental impact.
- Ease of Maintenance: Flooded lead-acid batteries can be maintained by checking and topping up the electrolyte.
Disadvantages of a Lead Acid Battery
- Heavy and Bulky: Lower energy density compared to modern battery technologies.
- Limited Lifespan: Prone to sulfation and reduced capacity over time, especially if not properly maintained.
- Slow Charging: Takes longer to recharge compared to lithium-ion batteries.
- Requires Maintenance: Regular electrolyte checks are needed for flooded types.
- Environmental Concerns: Lead and sulfuric acid pose environmental hazards if not properly recycled.
- Low Energy Efficiency: Relatively low charge/discharge efficiency.
Applications of a Lead Acid Battery
Following are some of the important applications of lead – acid batteries :
- As standby units in the distribution network.
- In the Uninterrupted Power Supplies (UPS).
- In the telephone system.
- In the railway signaling.
- In the battery operated vehicles.
- In the automobiles for starting and lighting.