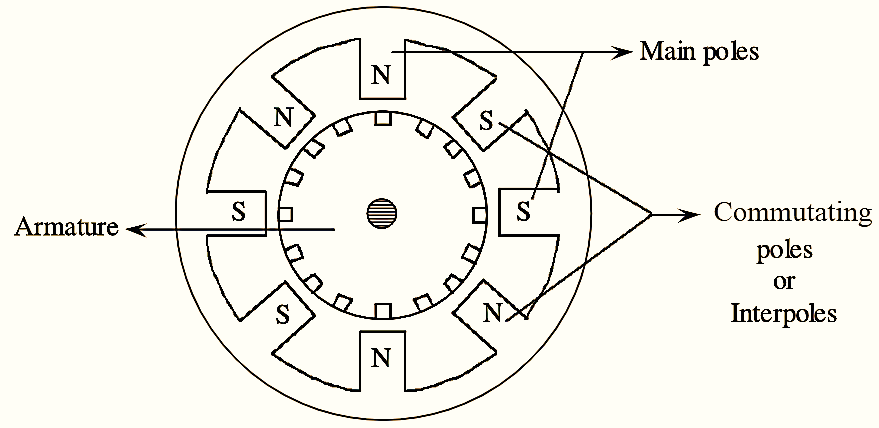
Figure 1: Interpoles.
Interpoles are small poles placed in between the main poles of a D.C generator as shown in figure (1). Interpoles are also known as commutating poles or com poles. In generators, the polarity of the inter pole is same as the main pole which is ahead of it in the direction of rotation. The following are the two functions performed by interpoles in a D.C generator.
- Neutralization of reactance voltage
- Neutralization of cross magnetizing effect of armature reaction.
Neutralization of Reactance Voltage :
When the position of brushes is fixed at GNA, then due to armature reaction, air gap flux which exists along GNA is also along brush axis or interpolar region. Reactance voltage is induced in the coil undergoing commutation due to the presence of air gap flux. This reactance voltage leads to delayed commutation and sparking at brushes. The function of interpoles or commutating poles is to generate e.m.f exactly in opposition to the reactance voltage, so that the effect of reactance voltage is nullified and the commutation process is improved. Also, as armature current increases, the air gap flux and there by reactance voltage increases. Therefore. the interpole winding is connected in series with armature so that commutating e.m.f also increases whenever there is a rise in armature current. This method of attaining sparkless commutation by using interpoles is known as voltage commutation.
Neutralization of Cross Magnetizing Effect of Armature Reaction :
Cross magnetizing effect of armature reaction in inter-polar region is minimized by interpoles. As interpoles are connected in series with armature windings the m.m.f produced by them opposes the m.m.f produced by armature conductor in interpolar region. If the armature current increases, the armature reaction also increases. Due to the series connection of armature and interpoles, the interpole m.m.f also increases proportionately with armature m.m.f but in opposite direction. The process of neutralization of cross magnetizing effect of armature reaction by using interpoles is as shown in figure (2).
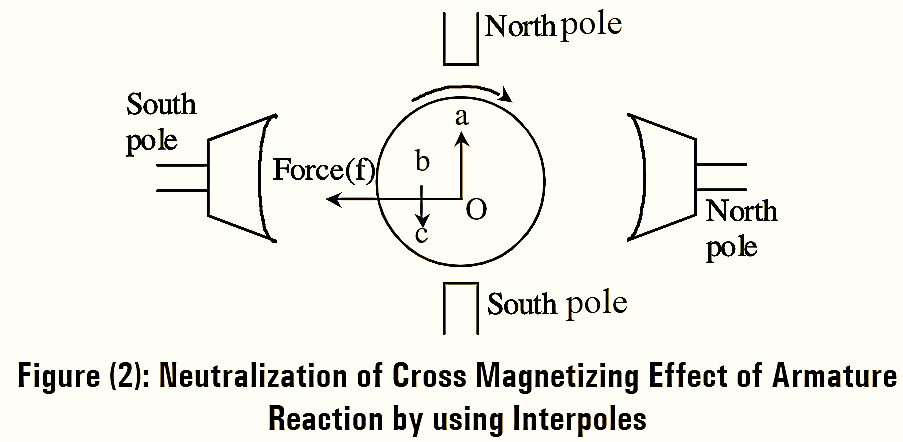
In the above figure 2,
Of represents m.m.f due to main poles
Oa represents cross magnetizing m.m.f due to armature
bc represents m.m.f due to interpoles.
As bc is in opposite direction to Oa, the m.m.f due to interpoles cancels out cross magnetizing m.m.f.