The armature control method works on the principle that the speed of the DC motor could be varied by varying the back emf.
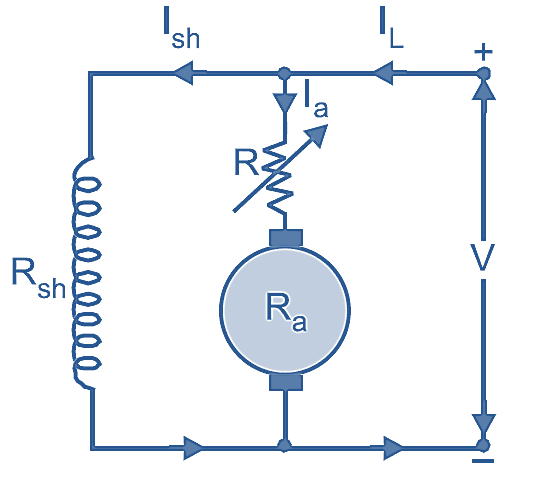
Fig. 1: Armature Control Method of DC Motor.
Working and Diagram of Armature Control Method
As the back emf in DC motor, Eb = V – Ia Ra, by varying the armature resistance we can obtain various speeds. A variable resistance (R) called controller is connected in series with the armature as shown in Fig 1. The controller should be selected to carry the armature current for a longer period. Let the initial and final speeds of the motor be N1 and N2, and the back emf be Eb1 and Eb2 respectively,
\[{{N}_{2}}=\frac{{{E}_{b2}}{{N}_{1}}}{{{E}_{b1}}}\]
By varying the controller resistance (R) value in the armature circuit, the back emf can be varied from Eb1 to Eb2, thereby, the speed can be varied from N1 to N2.
Advantages of Armature Control Method
This method is suitable for constant load drives where speed variations from low speed up to normal speed are only required.
Disadvantages of Armature Control Method
- Speeds below normal can only be obtained.
- A stable speed cannot be maintained when the load changes.
- Power loss in the control resistance is high due to the higher current rating, leading to the low efficiency of the motor.
- The cost of control resistance is high due to the fact it has to be designed to carry the armature current.
- Requires expensive arrangements to dissipate the heat developed in the control resistance.
Application of Armature Control Method
Suitable for DC shunt and compound motors used in printing machines, cranes, and hoists where the duration of low-speed operation is minimum.