Synchronous Motor needs initial starting torque. For this purpose different methods can be used.
Methods
- Use of damper winding
- Use of pony-motor
- Use of small induction motor
- Starting as slip-ring induction motor.
Using Damper Winding
In rotor pole shoe part, copper bars are put These copper bars are shorted at both ends by means of end ring. The construction of rotor is similar to induction motor’s rotor (squirrel cage type). So this motor can now start as an induction motor. The induction motor is self start motor.
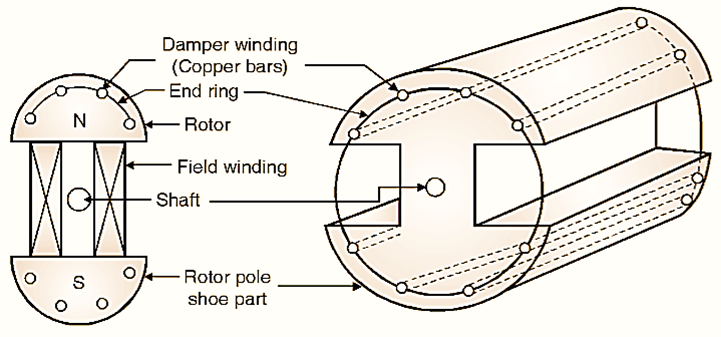
Fig. 1: Damper winding location
The rotor now, runs at a speed slightly less than synchronous speed (i.e. stator moving field). And then magnetic locking takes place automatically and motor now runs as a synchronous motor.
Damper winding e.m.f
The speed of stator rotating magnetic field is N and that of rotor is N. At start, the rotor speed N = 0 since rotor is at rest So relative speed is (Ns – N) = Ns. The damper winding cuts the rotating magnetic field of stator and due to electromagnetic induction an e.m.f is induced in it. This e.m.f is proportional to (Ns – N). The relative speed (Ns – N) is maximum at start so e.m.f in damper winding will be maximum. As the motor gathers speed, N increases and relative speed (Ns – N) decreases. The damper winding e.m.f will also decrease under running condition.
Using Pony Motor
Pony motor is a small DC shunt motor. It is mechanically coupled to rotor of synchronous motor. The pony motor rotates the rotor at synchronous speed. The magnetic locking takes place and motor now runs as a synchronous motor. After this, the pony motor’s DC supply is made OFF so pony motor will not play any role in running condition k is used just for the sake of starting the synchronous motor.
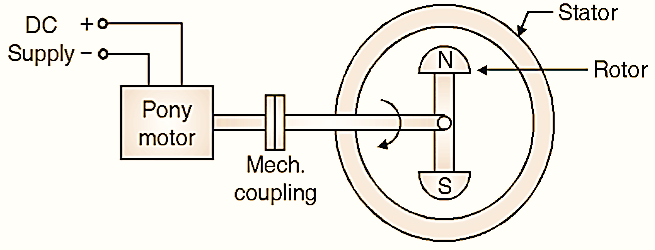
Fig. 2: Using pony motor
Using Small Induction Motor
Arrangement is similar to previous method. An induction motor is used (squirrel cage type) to give initial rotation. Once the speed is developed and poles are magnetically coupled, the induction motor is mechanically de-coupled and motor runs as synchronous motor at a constant speed (Ns = 120.f / P ) (See Fig. 3).
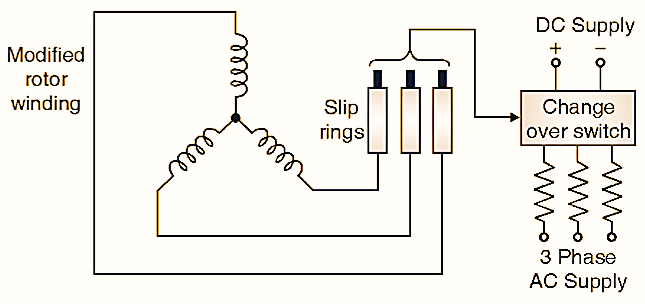
Fig. 3 : Use of small induction motor
Starting it as Slip-Ring Induction Motor
The synchronous motor is made to start as an slip-ring induction motor. The rotor winding needs some modification. 3 phase supply is connected to rotor by means of change over switch. The motor starts as an induction motor. It runs near synchronous speed, then DC supply is connected, now it runs as a synchronous motor. This method is not used in practice because of complications in field winding. The damper winding method is most popular for starting of synchronous motor.
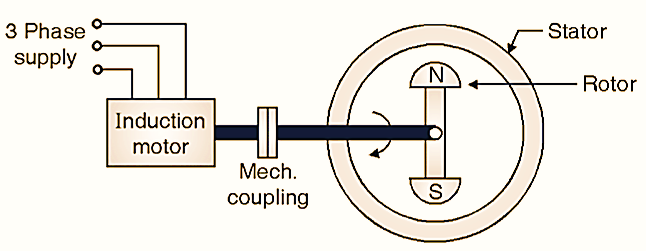
Fig. 4 : Starting it as slip-ring induction motor.