A Split Phase Induction Motor is a type of single-phase motor that has two windings: a main winding and a starting winding. The primary feature of this motor is its ability to create a phase difference between the currents in the main and starting windings, which helps generate the necessary starting torque.
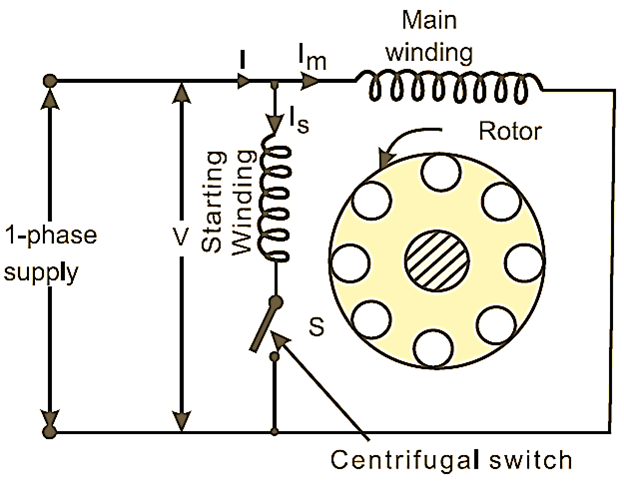
Fig. 1. Split phase motor.
Construction of Split Phase Induction Motor
Stator: The stator contains two windings and both windings are mounted in the stator slots:
-
-
- Main Winding: Connected directly to the power supply.
- Starting Winding: Positioned 90° electrically apart from the main winding and connected in series with a starting switch.
-
Rotor: The rotor is of the squirrel cage type, which consists of aluminum or copper bars short-circuited at both ends.
Centrifugal Switch: A mechanical switch installed in series with the starting winding. It disconnects the starting winding once the motor reaches 70-80% of its rated speed.
Working Principle of Split Phase Induction Motor
When a single-phase supply is given, the main winding and starting winding create a phase difference in currents. This phase difference produces a rotating magnetic field that starts the motor. Once the motor reaches a sufficient speed (typically 70-80% of its rated speed), the centrifugal switch opens and disconnects the starting winding, leaving only the main winding to maintain the operation.
Working of Split Phase Induction Motor
Split Phase Induction Motor is a type of A.C. single phase motor. It has two windings placed at 90° to each other. These are starting winding and main windings. The main winding has low resistance and high inductance. It is wound with thick conductor having less number of turns then the starting winding. It is embedded in the slots. The starting winding has more resistance and low inductance. It is done with thin conductor having more number of turns or some times equal. It is done on the upper side of the running winding.
The electrical angular displacement between these two windings is 90° electrical as shown in Fig. 1. The currents of both windings differ in value and phase. The current of starting winding Is is near to the voltage vector because of more resistance and current of main winding Im is towards lagging side because of more inductance. The main winding is connected across the line where the starting winding only for the starting period. The starting winding is disconnected from the mains by the centrifugal switch.
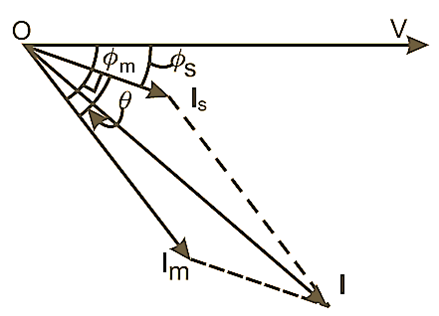
Fig. 2. Vector diagram.
Working of Split Phase Induction Motor
When the motor is connected across the supply the starting winding because of more resistance draws current at a phase difference near to the voltage vector. The main winding because of more inductance draws current on the lagging side, away from the voltage vector as shown in Fig. 2. There are two currents, resulting two magnetic fields which produces the magnetic field of rotating in nature. Hence the motor starts. As the motor attains its 75% of the synchronous speed, the centrifugal switch disconnect the starting winding and now motor is running on main winding only.
Characteristics of Split Phase Induction Motor
- Torque: The starting torque is low. It is about 1.3 to 1.7 the full load torque. The torque increases with the increasing of load as shown in Fig. 1.
- Current: The starting current is approximately five times the full load current. Without load, current is minimum and increases with the increasing of load.
- Speed: The speed at no load is approximately equal to the Synchronous speed and slightly falls down with the increasing of road.
- Power factor: The power factor is low i.e. 0.6 to 0.8 lagging.
- Efficiency: The efficiency of the motor is low as compared with the three phase induction motors.
Advantages of Split Phase Induction Motor
- Simple Design: The construction is simple and easy to manufacture.
- Low Cost: Cheaper compared to other single-phase motors like capacitor-start motors.
- Moderate Starting Torque: Suitable for applications where high starting torque is not required.
- Reliable Operation: Robust and durable due to its simple mechanical and electrical design.
Applications of Split Phase Induction Motor
- Fans: Ceiling fans, table fans, and exhaust fans.
- Pumps: Water pumps for domestic and agricultural use.
- Blowers: Small blowers and ventilators.
- Small Machinery: Used in small lathes and drill presses.
- Appliances: Washing machines and other small household equipment.