A Shackle Insulator, also known as a spool insulator, is a type of low-voltage electrical insulator commonly used in distribution networks to support and insulate conductors. Shackle insulators are compact, durable, and designed for horizontal or vertical mounting on poles or walls. They are widely utilized for low voltage (up to 33 kV) applications, particularly in urban and rural power distribution.

Construction of Shackle Insulator
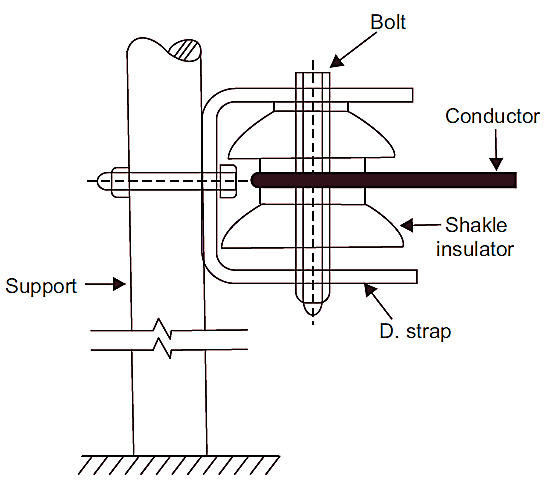
- Insulating Material: The main body is made of porcelain, ceramic, or polymer materials. These materials are selected for their high electrical and mechanical strength.
- Metal Components: A metal bolt or stud passes through the central hole of the insulator, attaching it to the supporting structure. The conductor is secured using metal clamps, bolts, or straps.
- Groove for Conductor: The insulator has a groove or channel around its circumference where the conductor is placed and bound using wire or straps.
- Shape and Design: Typically shaped like a spool or reel, which helps in compact installation and reduces space requirements. Sheds or ribs may be present to improve the creepage distance and prevent surface leakage during wet conditions.
Working of Shackle Insulator
- Support and Insulation: The conductor is placed in the groove of the insulator and secured tightly using binding wire or a metal strap. The shackle insulator provides mechanical support to the conductor and electrical insulation between the conductor and the supporting structure.
- Preventing Leakage: The insulating material prevents the flow of electric current to the pole or wall, ensuring proper insulation. The shape and design prevent the accumulation of water, dirt, or pollutants that can cause leakage current.
- Handling Mechanical Loads: The insulator can handle both horizontal and vertical mechanical loads due to its robust construction.
Types of Shackle Insulators
- Porcelain Shackle Insulators:
- Made of glazed porcelain, which is durable and weather-resistant.
- Commonly used in traditional distribution systems.
- Polymer Shackle Insulators:
- Made of polymer materials like silicone rubber.
- Lightweight, high-strength, and resistant to pollution.
Advantages of Shackle Insulators
- Compact Design: Small and lightweight, making them ideal for space-constrained installations.
- Cost-Effective: Affordable and widely available, especially for low-voltage applications.
- Easy Installation: Simple to mount and maintain using bolts, clamps, or straps.
- Durability: Resistant to environmental factors such as rain, dust, and heat, especially in porcelain and polymer designs.
- Versatility: Can be used for both horizontal and vertical mounting.
- Reliable Performance: Provides consistent electrical insulation and mechanical support in low-voltage systems.
Disadvantages of Shackle Insulators
- Limited Voltage Range: Not suitable for high-voltage applications due to size and design constraints.
- Mechanical Stress: Not ideal for systems with heavy mechanical stress or tension in conductors.
- Fragility: Porcelain shackle insulators are prone to cracking or breakage under high impact.
- Corrosion: Metal parts like bolts and straps can corrode over time in harsh environments.
- Creepage Distance: Limited creepage distance, making them less effective in polluted or highly humid environments.
Applications of Shackle Insulators
- Low Voltage Distribution Networks: Commonly used in both urban and rural distribution systems for voltages up to 33 kV.
- Service Connections: Widely used for supporting service wires leading to buildings.
- Wall and Pole Mounting: Used in installations where conductors are supported on walls or poles.
- Industrial Power Distribution: Employed in small-scale industrial setups for power distribution.
- Overhead Lines: Used in low-voltage overhead distribution lines to insulate and support conductors.
Conclusion
The shackle insulator is an essential component of low-voltage distribution systems due to its simplicity, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. Its compact design and ability to handle mechanical loads make it suitable for a wide range of applications, from urban power distribution to service connections in rural areas. However, its limitations in high-voltage systems and susceptibility to environmental degradation in some designs should be considered when selecting an insulator type for specific applications.