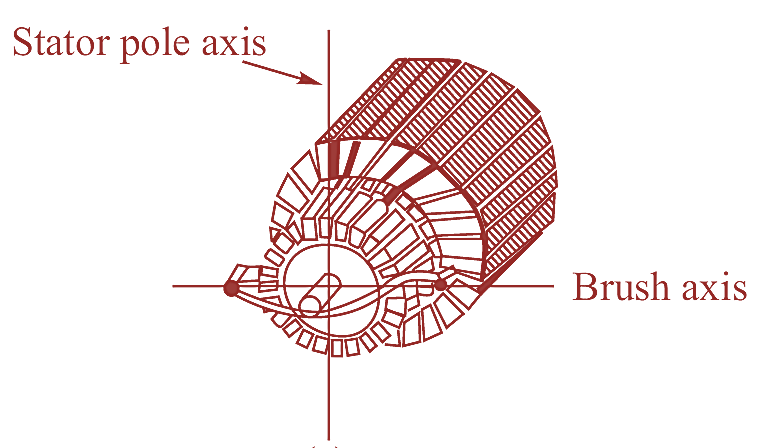
Construction of Repulsion Motor
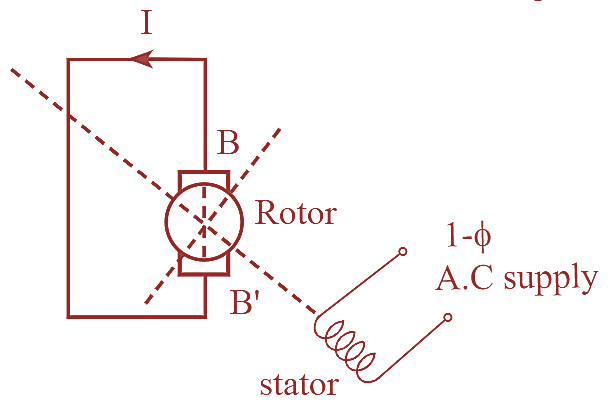
Figure 1: Repulsion Motor.
Repulsion motor is a type of A.C commutator motor which consists of a single phase winding placed in stator slots and the rotor carrying a distributed winding connected to the commutator at one end. The surface of the commutator bars is in contact with brushes which are short circuited as shown in figure 1.
Working Principle of Repulsion Motor.
The principle of operation of repulsion motor is the repulsion between the two magnetic fields i.e., like magnetic poles repel each other.
When the stator winding of a motor is connected to A.C supply, it produces a magnetic field in the poles which is alternating in nature. Due to this alternating field, a voltage is induced in the armature windings. When the brushes are located properly the current flows through the armature winding, so that a magnetic field of same polarity is produced in the armature. The stator magnetic field repels the armature magnetic field and hence the rotor starts rotating.
Working of Repulsion Motor
When the stator winding of a motor is connected to A.C supply, it produces a magnetic flux in the poles which is alternating in nature. Due to transformer principle, an e.m.f is induced in the armature conductors. The direction of the induced e.m.f can be obtained by using Lenz’s law. However, the direction of the induced currents depend on the position of the brushes.
When the brushes are in normal position i.e., perpendicular to the main field flux, the field flux tries to balance the armature flux such that the resultant e.m.f becomes zero and no current flows in the armature winding. Hence, there is no torque developed. When the brushes are along the field axis, the main field flux tries to oppose the rotor flux so that a maximum current flows through the winding. Due to the lack of relative motion between the stator and the rotor fluxes, the rotor fails to move and hence there is no torque developed. If the brushes are located such that the axis of the brush is neither along the field axis and nor perpendicular to the field axis i.e., the brush axis makes an angle with the field axis, an e.m.f will induce between the terminals of the blushes due to which the current flows through the winding. Now, the armature will again act as an electromagnet by developing its own north and south poles. The N-pole of the rotor gets repelled by the N-pole of the main field. Similarly the S-pole of the rotor will be repelled by the S-pole of the stator. Hence, the rotor rotates in clockwise direction.
Advantages of Repulsion Motors
The following are the advantages of repulsion motors.
- They have very high starting torque.
- The starting current is low in these motors.
- They have wide range of speed control.