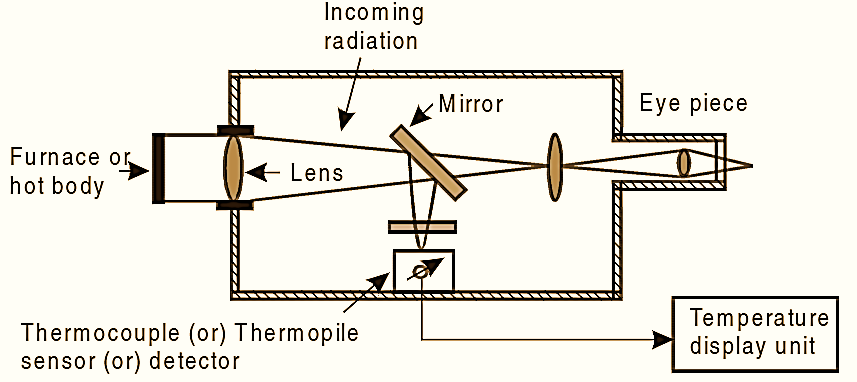
Figure 1: Radiation Pyrometer.
A total radiation pyrometer is used to measure the temperature by evaluating the heat radiation emitted by a body. All the radiations emitted by a hot body or furnace flames are measured and calibrated for black-body conditions.
Working Principle of Radiation Pyrometer
Every object radiates thermal energy at temperatures above absolute zero and the radiation emitted is a function of its temperature. The energy radiated is proportional to the emissivity at a particular temperature and wavelength. To measure the accurate temperature of a given surface from which radiation is receiving, an operator has to know the emissivity of that material. The radiation is focussed using a lens onto sensor which is a photo sensitive device and generates a voltage proportional to the radiation falling on it (Thermal detector).
Construction of Radiation Pyrometer
A total radiation pyrometer (see Fig. 1) consists of an optical system which includes a lens, a minor, and an adjustable eyepiece. The radiation heat energy emitted from the hot body is focused by an optical system onto a thermocouple or a thermopile and converted to its analogous electrical signal and can be read on a temperature display unit.
The pyrometer should be aligned properly with hot body and should be placed as close to it as possible to minimize the absorption of radiation by the atmosphere. Radiation pyrometers are useful for the measurement of temperature in corrosive environments and in applications where physical contact is impossible.
Advantages of Radiation Pyrometer
- It is a non-contact-type device.
- Very quick response is possible.
- Suitable for high-temperature measurement.
Disadvantages of Radiation Pyrometer
- Due to emission of radiations to the atmosphere. errors in temperature measurement are possible.
- Errors due to emissivity affect measurements.