Plate earthing is a method of grounding electrical systems by burying a metallic plate deep into the ground to provide a low-resistance path for fault currents. This ensures the safety of electrical equipment and personnel by preventing electric shocks and minimizing voltage fluctuations.
Parts of Plate Earthing System
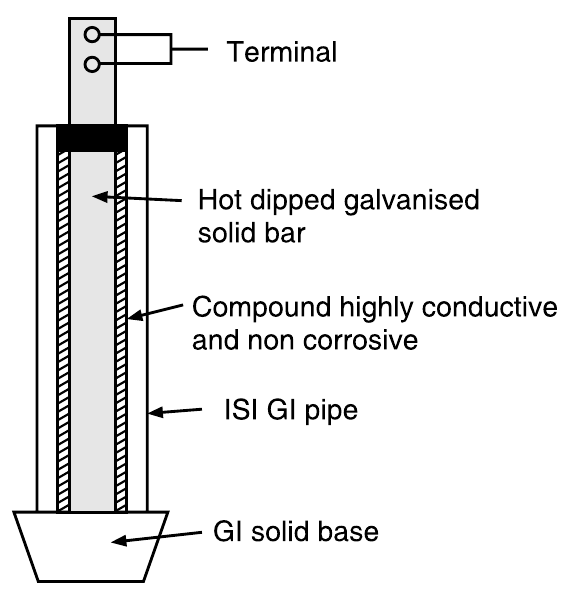
- Earth Plate: A copper or galvanized iron (GI) plate is used, usually measuring 600 mm x 600 mm x 3 mm for copper and 600 mm x 600 mm x 6 mm for GI.
- Earth Pit: A dugout area where the plate is buried, typically 2-3 meters deep.
- Earthing Electrode: A conductive material that ensures contact with the soil and helps dissipate electrical energy.
- Earthing Wire: Copper or GI wire connects the plate to the electrical system.
- Moisture Retaining Material: Charcoal and salt are used to maintain soil moisture, improving conductivity.
- Watering Pipe: A GI pipe allows water to be poured into the pit to maintain moisture.
- Earth Pit Cover: A concrete or cast iron cover is used to protect the earthing setup from damage.
Procedure for Plate Earthing
- Excavation: Dig a pit of about 2-3 meters deep.
- Plate Placement: Place a copper or GI plate vertically in the pit.
- Connecting Wire: Attach the earthing wire to the plate using welding or a bolt.
- Filling with Charcoal and Salt: Surround the plate with alternate layers of charcoal and salt for moisture retention.
- Watering Pipe Installation: Place a GI watering pipe beside the plate for maintaining moisture.
- Backfilling: Cover the pit with soil to complete the setup.
- Pit Covering: Place a cover to protect the earthing pit.
- Testing: Check the resistance using an earth resistance tester to ensure effectiveness.
Advantages of Plate Earthing
- Low Resistance Path: Provides efficient grounding for electrical systems.
- Long-Lasting: With proper maintenance, plate earthing systems can last for years.
- Reliable Performance: Ensures safe dissipation of fault currents.
- Suitable for High Load Systems: Can handle large electrical loads effectively.
- Minimal Maintenance: Requires periodic watering but has low overall maintenance costs.
Disadvantages of Plate Earthing
- High Installation Cost: Requires extensive digging and materials like copper plates.
- Space Requirement: Needs a large area for effective installation.
- Soil Dependency: Effectiveness depends on soil moisture and conductivity.
- Regular Maintenance: Needs frequent watering to maintain conductivity.
Applications of Plate Earthing
- Industrial Installations: Used in factories, substations, and power plants for electrical safety.
- Commercial Buildings: Ensures safety in large office spaces.
- Residential Buildings: Protects home appliances and electrical systems.
- Telecommunication Towers: Provides grounding for communication equipment.
- Lightning Protection Systems: Used in grounding lightning arresters to prevent damage.
- Data Centers: Ensures proper earthing for sensitive electronic equipment.
Difference Between Pipe Earthing and Plate Earthing
| Feature | Pipe Earthing | Plate Earthing |
|---|---|---|
| Electrode Used | GI or Copper Pipe | GI or Copper Plate |
| Installation Depth | 2.5 to 3 meters | 2 to 3 meters |
| Maintenance | Requires less maintenance | Needs frequent watering |
| Cost | Lower compared to plate earthing | Higher due to materials and labor |
| Efficiency | Moderate | High |
Conclusion
Plate earthing is one of the most effective methods for grounding electrical systems. Although it requires careful installation and maintenance, its advantages outweigh the drawbacks, making it a preferred choice for various applications. By providing a low-resistance path to dissipate fault currents safely, plate earthing plays a crucial role in electrical safety and system reliability.