An off-grid solar system is a standalone power system that operates independently of the utility grid. It uses solar panels to generate electricity, which is stored in batteries for use when sunlight is unavailable. These systems are designed to provide electricity in remote or rural areas where grid power is inaccessible or unreliable. Off-grid systems are fully self-sufficient and are not connected to the main electricity grid.
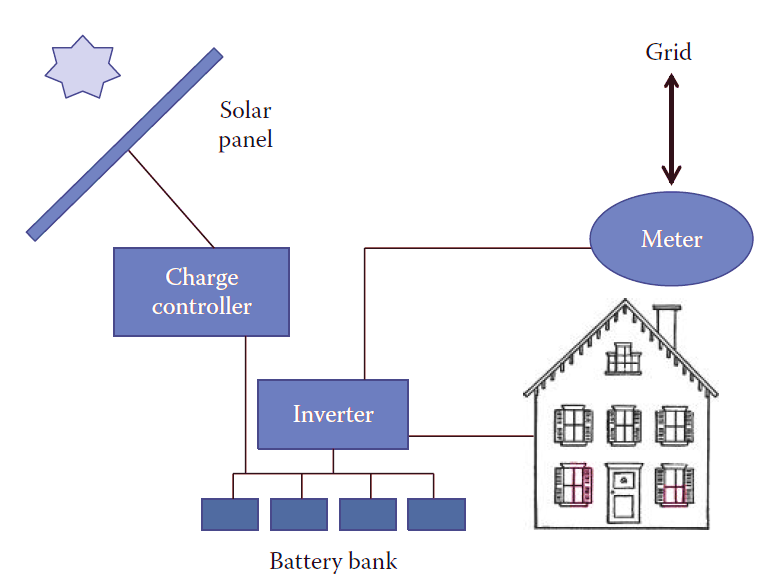
Components of an Off-Grid Solar System
Solar Panels:
-
- Purpose: Capture sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity using photovoltaic (PV) cells.
- Types: Monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film panels.
- Placement: Typically installed on rooftops or open areas to maximize exposure to sunlight.
Charge Controller:
-
- Function: Regulates the voltage and current coming from the solar panels to the battery bank to prevent overcharging and over-discharging.
- Types: Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) and Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT).
Battery Bank:
-
- Purpose: Stores the electricity generated by solar panels for use during the night or cloudy days.
- Types: Lead-acid, lithium-ion, and gel batteries.
- Capacity: Determines how long the system can supply power without sunlight.
Inverter:
-
- Function: Converts the DC electricity from the batteries into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is used by most household appliances.
- Types: Pure sine wave and modified sine wave inverters.
Meter:
-
- Purpose: Measures energy consumption and monitors the performance of the system.
- Role: Useful for optimizing energy usage and maintenance.
Load (Household Appliances):
-
- Definition: Electrical devices and appliances powered by the system.
- Examples: Lights, fans, refrigerators, and other household electronics.
Backup Generator (Optional):
-
- Purpose: Acts as an additional energy source during extended periods of low sunlight or high energy demand.
- Fuel Source: Diesel, gasoline, or natural gas.
Difference between Off Grid Solar System and On Grid Solar System
| Feature | Off-Grid Solar System | On-Grid Solar System |
|---|---|---|
| Grid Connection | Operates independently of the utility grid. | Connected to the main electricity grid. |
| Energy Storage | Requires batteries for energy storage. | Excess energy is sent to the grid; no batteries needed. |
| Backup Energy | Backup generator often required. | Grid acts as a backup energy source. |
| Initial Cost | High due to batteries and additional components. | Lower as no batteries are required. |
| Suitability | Ideal for remote areas without grid access. | Suitable for areas with reliable grid access. |
| Energy Export | No surplus energy export. | Surplus energy can be fed back to the grid. |
Advantages of Off Grid Solar Systems
- Energy Independence:
- Fully self-sufficient and not reliant on the utility grid.
- Ideal for remote locations with no grid access.
- Eco-Friendly:
- Reduces carbon emissions and dependence on fossil fuels.
- Promotes the use of renewable energy.
- Reliability:
- Provides electricity even during power outages or grid failures.
- Suitable for areas prone to frequent outages.
- Scalability:
- Systems can be customized and expanded based on energy requirements.
- Modular designs allow easy upgrades.
- Cost-Effective in Remote Areas:
- Avoids the high cost of extending grid infrastructure to isolated locations.
- Long-term savings on electricity bills.
- Encourages Sustainability:
- Promotes energy conservation and responsible usage.
Disadvantages of Off Grid Solar Systems
- High Initial Cost:
- Requires significant investment in solar panels, batteries, and other components.
- Maintenance and replacement of batteries add to long-term costs.
- Energy Storage Dependency:
- Performance heavily relies on battery storage, which has limited capacity and lifespan.
- Batteries are prone to degradation over time.
- Weather Dependence:
- Solar generation is affected by weather conditions, such as cloudy or rainy days.
- Extended periods of bad weather may require backup energy sources.
- Complex Installation:
- Requires careful planning and skilled professionals for design and installation.
- Mistakes in sizing or configuration can lead to inefficiency or system failure.
- Space Requirements:
- Requires ample space for solar panel installation and battery storage.
- May not be suitable for urban or densely populated areas.
- No Grid Backup:
- Unlike hybrid systems, there is no connection to the grid for emergencies or surplus energy usage.
Applications of Off Grid Solar Systems
- Residential Use:
- Provides power for homes in rural or remote areas without grid access.
- Used for lighting, cooling, heating, and powering household appliances.
- Rural Electrification:
- Supplies electricity to off-grid villages and communities.
- Improves quality of life and access to education, healthcare, and communication.
- Agriculture:
- Powers irrigation systems, water pumps, and farming equipment.
- Reduces dependency on diesel generators in remote farming areas.
- Telecommunication:
- Supplies energy for telecommunication towers and remote communication systems.
- Healthcare:
- Provides electricity to rural clinics and hospitals for medical equipment and refrigeration of vaccines.
- Military and Emergency Services:
- Powers remote military bases, disaster relief operations, and emergency shelters.
- Recreational and Mobile Applications:
- Used in RVs, boats, and camping setups for portable power needs.
- Ideal for eco-tourism and sustainable travel.
- Industrial Use:
- Supplies energy for small-scale industries and workshops in remote areas.
- Powers mining, oil, and gas operations in isolated regions.
Conclusion
An off-grid solar system is a reliable and sustainable solution for powering areas without access to the grid. While it offers energy independence, scalability, and eco-friendliness, the high initial costs, dependency on weather, and energy storage limitations must be carefully considered. Off-grid systems are widely used in residential, agricultural, healthcare, and industrial applications, playing a significant role in promoting renewable energy and reducing carbon footprints globally.