Lead sheathed wiring is a type of electrical wiring system that uses conductors insulated with rubber and enclosed in a lead-aluminum alloy sheath. This system provides excellent mechanical protection and resistance to environmental factors such as moisture and corrosive gases. It was commonly used in industrial and residential applications in the past but has now been largely replaced by modern alternatives.
What is Lead Sheathed Wiring?
Lead sheathed wiring is an electrical wiring system where conductors are insulated with Vulcanized Indian Rubber (VIR) or Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) and enclosed in a sheath made of lead-aluminum alloy. This sheath protects the wiring from mechanical damage, moisture, and corrosive elements, making it suitable for specific industrial and underground applications.
Parts of Lead Sheathed Wiring
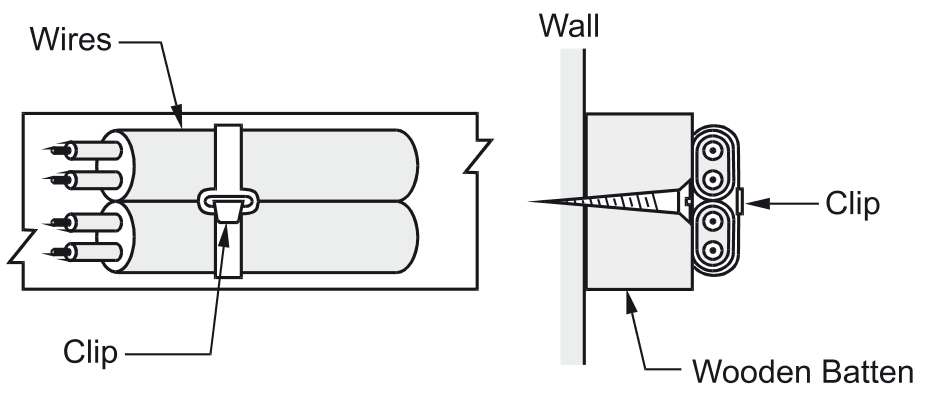
- Wires (Conductors): Copper or aluminum wires used for carrying electrical current.
- Rubber or PVC Insulation: Provides electrical insulation to prevent short circuits and leakage.
- Lead Sheath: An outer protective covering made of lead-aluminum alloy that shields the wires from mechanical damage and environmental conditions.
- Clips and Saddles: Used to secure the lead sheathed cables to walls or wooden battens.
- Wooden Batten: A strip of wood fixed to the wall to support and organize wiring installations.
- Wall or Surface: The structure where the wiring is installed, typically in industrial buildings and underground systems.
Working Principle of Lead Sheathed Wiring
- The wires are insulated with rubber or PVC to ensure electrical safety.
- A lead-aluminum alloy sheath is applied around the insulated wires to provide additional protection.
- The lead sheath shields the wiring from environmental elements such as moisture, chemicals, and mechanical damage.
- Clips and saddles secure the sheathed wiring onto walls or wooden battens, ensuring proper alignment and safety.
- Electrical connections are made through junction boxes and switches as per the circuit requirements.
Advantages of Lead Sheathed Wiring
- Excellent Mechanical Protection: The lead sheath protects the wiring from external physical damage.
- Moisture Resistance: Highly resistant to moisture, making it suitable for damp environments.
- Corrosion Protection: The lead sheath prevents chemical corrosion, ideal for industrial setups.
- Long Lifespan: More durable compared to ordinary wiring systems under suitable conditions.
- Safe Installation: Provides insulation against electric shocks and short circuits.
- Fire Resistance: The lead sheath offers protection against fire hazards to some extent.
Disadvantages of Lead Sheathed Wiring
- High Cost: Lead sheathed cables are expensive due to material and installation costs.
- Heavy Weight: The lead covering adds significant weight, making installation difficult.
- Difficult to Modify: Changes or extensions to the wiring system require considerable effort.
- Health and Environmental Concerns: Lead is a toxic material, posing risks during installation and disposal.
- Outdated Technology: Modern alternatives such as PVC and XLPE insulated cables have largely replaced lead sheathed wiring.
- Limited Flexibility: The rigid structure makes it less adaptable for modern wiring needs.
Applications of Lead Sheathed Wiring
- Underground Installations: Used for power transmission in underground electrical networks.
- Industrial Plants: Suitable for factories and manufacturing units where moisture and chemicals are present.
- Damp and Corrosive Environments: Applied in chemical plants and marine environments.
- Power Distribution Systems: Utilized in power plants and substations for high-reliability circuits.
- Older Residential and Commercial Buildings: Found in older structures where lead sheathed wiring was once standard.
Conclusion
Lead sheathed wiring was an advanced method of electrical wiring that offered superior mechanical and environmental protection. However, due to its cost, weight, and health concerns, it has been largely replaced by modern wiring solutions. While it is still used in specific industrial and underground applications, newer technologies provide more efficient and safer alternatives for electrical wiring.