An inductor is a coil or electromagnetic device that oppose any change in current. Inductors or coils, probably vary more in design than any other component. Basically, an inductor is a conducting wire wound on an insulator. Inductor is the name of a component. Its value is called as inductance.
Construction and Symbol of Inductor
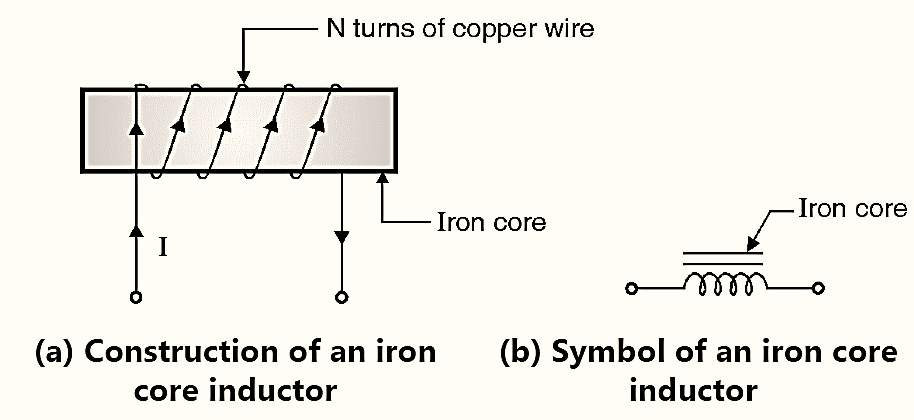
Figure 1: Inductor.
Fig. 1(a) shows the construction of an inductor and Fig. 1(b) shows its symbol. It is a fixed value inductor. An inductor consists of N turns of a laminated copper wire are wound around an iron core.
Unit of Inductor
Inductance is measured in Henry or millihenry or microhenry and it is denoted by L. Henry is a very large unit. Therefore millihenry and microhenry are the another small units used for inductors.
\[\text{1 mH = 1 }\times \text{ 1}{{\text{0}}^{-\text{3}}}\text{ H}\]
\[\text{1 }\!\!\mu\!\!\text{ H = 1 }\times \text{ 1}{{\text{0}}^{-6}}\text{ H}\]
The inductance of a coil is given by,
\[\text{L = }\frac{N\times \phi }{I}\]
Where,
N = Number of turns,
ϕ = Flux
I = Current through the coil.
So the factors affecting the inductance are number of turns, flux linkage and current.
Types of Inductor
Inductors are basically categories,
- Fixed inductors.
- Variable inductors.
1. Types of Fixed Inductor :
The fixed inductors are classified as follows:
- Air-core inductor.
- Iron-core inductor.
- Ferrite-core inductors.
1. Air-core inductor :
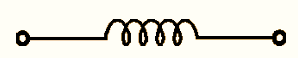
(a) Symbol
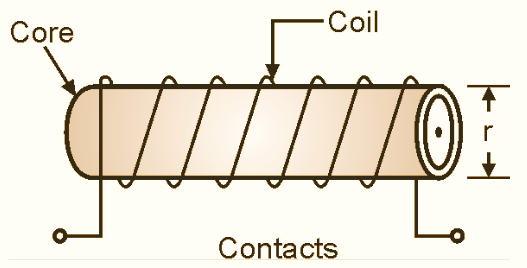
(b) Construction
Figure 2: Air-core Inductor.
In this inductor, the coil is wound on a plastic or cardboard core. Therefore, effectively the air acts as core. The symbol of air core inductor is shown in Fig. 2.
Construction :
The construction of an air-core inductor is shown in Fig. 2. In the construction of air core inductors, a core is made up of ceramics, plastic or cardboard type insulating material. The conductive wire is wound on this core hence there is air inside the coil.
Applications :
- They are used for intermediate or radio frequency (I.F. or R.F.) applications in tuning coils.
- For inter-stage coupling.
- IF. coils.
- Iron-core inductor :
2. Iron-core inductor :
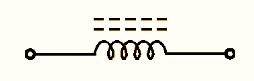
(a) Symbol
(b) Construction
Figure 3: Iron core Inductor.
An iron core inductor is a coil in which solid or laminated iron or other magnetic material forms a part or all of the magnetic circuit linking its winding. It is also known as iron-core choke. Iron core inductors have a high inductance value but they cannot operate at high frequency due to hysteresis and eddy current losses. Iron core increases the magnetic induction of a coil of wire. Because iron has high permeability, it allows more magnetic lines of flux to concentrate the core thereby increasing the electromagnetic induction.
Construction :
Iron core inductor consists of coil wound over a solid or laminated iron core. The construction of iron core inductor is shown in Fig. 3. The material used for the iron core inductor is Silicon steel which is composed of iron with some percent of silicon. The iron core is laminated to avoid eddy current losses. The laminated iron-core consists of thin iron laminations pressed together but insulated from each other. Low frequency iron cored chokes are used as filter chokes to smooth out ripple in the rectified ac supply amplifier stages and in other d.c. applications. The core materials most commonly used for smoothing chokes are, silicon iron laminations and grain oriented silicon iron.
Applications :
The iron core inductors are used in the dc power supply filter circuits and other low frequency applications.
3. Ferrite core inductor :
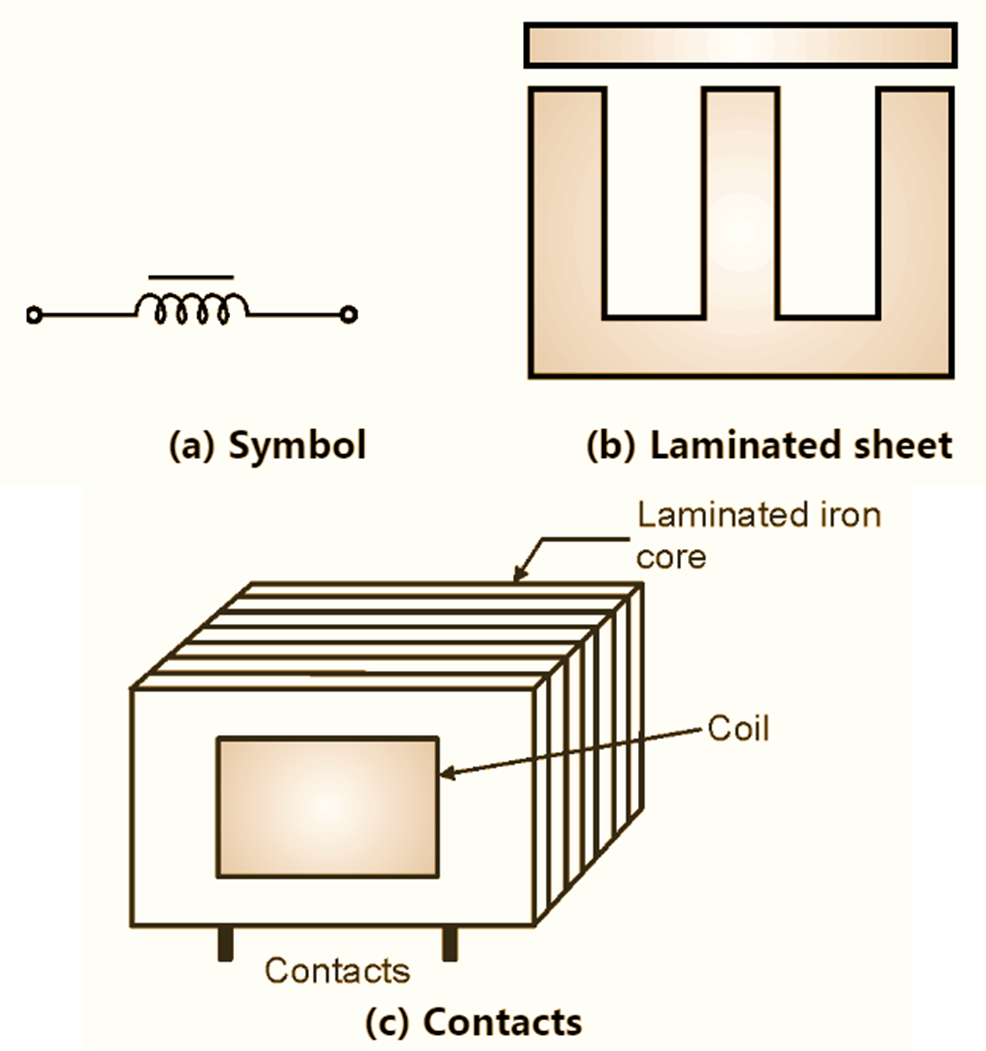
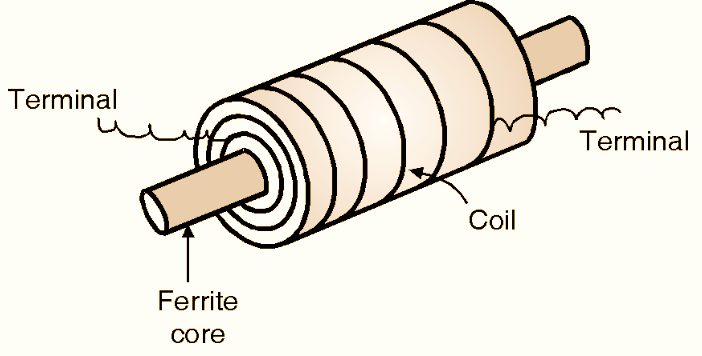
Figure 4: Ferrite core Inductor.
Ferrite is an artificially prepared non-metallic material using sintered iron oxide with other metal ions to control magnetic properties. If the coil of wire is wound on a solid core made of highly ferromagnetic substance called ferrite. Fig. 4 shows the symbol of ferrite core inductor. Ferrite is a ferrous magnetic material. In this type of inductor, wire is wound on a ferrite core.
Construction :
The construction of a ferrite core inductor is as shown in Fig. 4. Ferrites are ceramic materials composed of oxides of iron and other magnetic material. It is used at a high and medium frequency because it has high permeability with low loss, so it is more effective than iron core inductor. These inductors usually employ pot cores i.e. cores consisting of an outer cylinder with closed end. The winding is placed in annular space. The air- gap is introduced in the central core. We can choose a suitable length of this air gap, in order to change the properties of the pot to suit a wide range of design requirements.
Applications :
- These are used at high and medium frequencies.
- Ferrite rod antenna.
Specifications of inductor
- Inductance value.
- Q factor value.
- Operating frequency range.
- Power dissipation.
- Core type.
- Size and mounting requirements.
- Stary capacitance.