A Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV) is a type of vehicle that combines an internal combustion engine (ICE) with an electric motor to provide propulsion. HEVs use energy stored in batteries or other storage devices, as well as energy generated by the engine. The combination of both systems allows for improved fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and optimized performance, particularly in urban driving conditions.
Diagram of a Hybrid Electric Vehicle
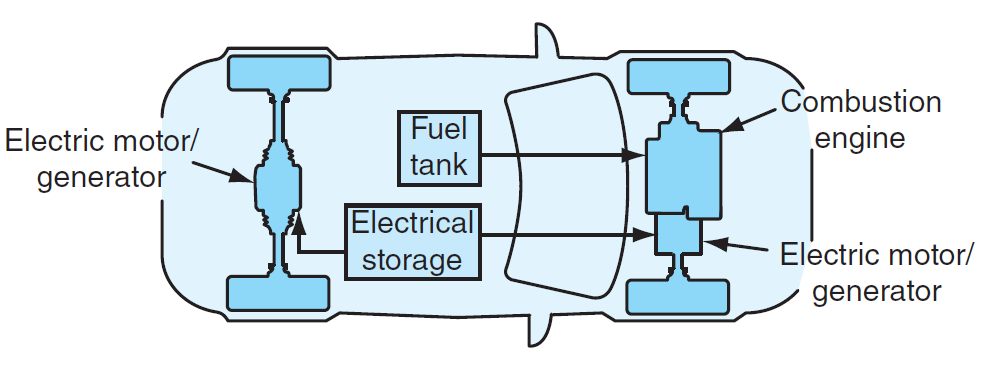
The following diagram illustrates the components and energy flow within a hybrid electric vehicle:
Key Components in the Diagram:
- Combustion Engine: Provides power during high-speed driving and long-range trips.
- Electric Motor/Generator: Supports propulsion and regenerative braking.
- Fuel Tank: Stores fuel for the ICE.
- Electrical Storage: Stores energy for the electric motor.
Construction of a Hybrid Electric Vehicle
The construction of an HEV integrates components from traditional internal combustion vehicles with electric propulsion systems. Key components of an HEV include:
- Internal Combustion Engine (ICE): Typically, a gasoline or diesel engine serves as the primary power source for extended range driving.
- Electric Motor/Generator: The electric motor drives the vehicle at low speeds or assists the ICE for additional power. It also acts as a generator during regenerative braking, converting kinetic energy back into electrical energy.
- Energy Storage System (Battery): The battery stores electrical energy generated during braking or produced by the engine and is used to power the electric motor.
- Fuel Tank: Stores conventional fuel (gasoline or diesel) for the internal combustion engine.
- Power Control Unit (PCU): Manages the distribution of power between the electric motor, battery, and internal combustion engine.
- Inverter/Converter: Converts direct current (DC) stored in the battery to alternating current (AC) for the motor and vice versa during regenerative braking.
- Transmission System: Transfers power from the ICE or electric motor to the wheels. It can be a conventional automatic, manual, or continuously variable transmission (CVT).
- Regenerative Braking System: Captures kinetic energy during braking and converts it into electrical energy to recharge the battery.
- Control System: Governs the interaction between the ICE, electric motor, and battery to ensure optimal efficiency and performance.
Working of a Hybrid Electric Vehicle
HEVs operate through a dynamic interaction between the internal combustion engine and the electric motor. The operation mode depends on driving conditions and power requirements:
- Startup and Low-Speed Operation: The electric motor is primarily used for propulsion at low speeds, minimizing fuel consumption and emissions.
- Acceleration: Both the ICE and electric motor work together to provide additional power for acceleration and high-speed driving.
- Steady Cruising: The ICE takes over as the primary power source, operating at optimal efficiency.
- Regenerative Braking: When the brakes are applied, the electric motor acts as a generator, converting kinetic energy into electrical energy to recharge the battery.
- Deceleration and Stopping: The electric motor and regenerative braking system work to decelerate the vehicle, reducing wear on traditional brake components.
- Idle Mode: The ICE shuts off during idling, relying on the battery and electric motor for auxiliary functions.
Advantages of Hybrid Electric Vehicles
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: By utilizing electric power for low-speed driving and regenerative braking, HEVs achieve higher fuel efficiency compared to conventional vehicles.
- Reduced Emissions: Lower greenhouse gas and pollutant emissions due to the reduced use of the ICE, especially in urban stop-and-go traffic.
- Energy Recovery: Regenerative braking recaptures energy that would otherwise be wasted as heat, improving overall energy efficiency.
- Quieter Operation: Electric motors provide silent operation, especially during low-speed driving.
- Flexibility: The combination of ICE and electric power ensures a longer range compared to fully electric vehicles.
- Reduced Dependency on Fossil Fuels: By relying partly on electric power, HEVs reduce overall fuel consumption.
- Lower Maintenance Costs: The reduced usage of the ICE leads to less wear and tear, lowering maintenance requirements over time.
Disadvantages of Hybrid Electric Vehicles
- High Initial Cost: The advanced technology and dual powertrain systems make HEVs more expensive than conventional vehicles.
- Complexity: The integration of ICE, electric motor, and battery systems increases complexity, requiring specialized maintenance.
- Battery Replacement Costs: Battery packs are expensive and may require replacement after extended use.
- Lower Performance: HEVs prioritize fuel efficiency over high-speed performance, which may not appeal to all drivers.
- Weight: The addition of batteries and electric components increases vehicle weight, potentially affecting handling.
- Limited Electric-Only Range: Standard HEVs cannot travel long distances on electric power alone, unlike plug-in hybrids or EVs.
Applications of Hybrid Electric Vehicles
HEVs are increasingly used across various sectors, owing to their versatility and efficiency:
- Personal Transportation: Hybrid cars, such as the Toyota Prius, are widely adopted by environmentally conscious consumers for daily commutes and long-distance travel.
- Public Transport: Hybrid buses and taxis reduce emissions in urban areas while offering reliable service.
- Commercial Fleets: Delivery trucks and logistics vehicles benefit from lower fuel consumption and reduced operating costs.
- Military Applications: HEVs are used in military vehicles for stealth operations and enhanced fuel efficiency.
- Agricultural Machinery: Hybrid tractors and equipment are employed for sustainable farming practices.
- Aviation: Hybrid technologies are being explored for use in small aircraft and drones to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions.
Types of Hybrid Electric Vehicles
| Type | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Micro Hybrid | Uses start-stop technology and regenerative braking but lacks an electric motor for propulsion. | Modern start-stop system vehicles |
| Mild Hybrid | Features an electric motor to assist the ICE but cannot operate solely on electric power. | Honda Insight, Suzuki Ciaz |
| Full Hybrid | Can operate on electric power, ICE, or a combination of both. | Toyota Prius, Ford Fusion Hybrid |
| Plug-In Hybrid (PHEV) | Includes a larger battery that can be recharged externally, offering extended electric-only range. | Chevrolet Volt, Toyota Prius Prime |
| Series Hybrid | The ICE acts as a generator to charge the battery, which powers the electric motor for propulsion. | BMW i3 (Range Extender) |
| Parallel Hybrid | The ICE and electric motor are both connected to the transmission to drive the wheels. | Honda Accord Hybrid, Hyundai Ioniq Hybrid |
| Series-Parallel Hybrid | Combines features of series and parallel hybrids for improved efficiency and flexibility. | Toyota Prius |
Future Trends in Hybrid Electric Vehicles
The evolution of HEV technology continues to focus on enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and integrating renewable energy sources. Future trends include:
- Improved Battery Technologies: Advancements in lithium-ion and solid-state batteries will enhance energy density, reduce weight, and lower costs.
- Electrification of Heavy-Duty Vehicles: Hybrid systems will be increasingly adopted in trucks, buses, and other heavy-duty vehicles.
- Integration with Renewable Energy: Plug-in hybrids may integrate with renewable energy systems for charging, further reducing their environmental impact.
- Enhanced Connectivity: Smart systems will optimize hybrid performance through real-time monitoring and predictive analytics.
- Autonomous Hybrid Vehicles: The combination of hybrid powertrains and autonomous driving technology will enable efficient, self-driving cars.
- Government Incentives: Policies promoting hybrid and electric vehicles will accelerate their adoption globally.
Conclusion
Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) represent a significant step forward in sustainable transportation, bridging the gap between traditional internal combustion engines and fully electric vehicles. By combining the strengths of both systems, HEVs offer improved fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and enhanced versatility. As advancements in hybrid technology continue, HEVs will play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of transportation.