A solar power plant is a facility that converts sunlight into electricity using photovoltaic (PV) technology or concentrated solar power (CSP). These plants are a clean and renewable source of energy, reducing carbon emissions and dependence on fossil fuels. Solar power plants are designed for large-scale electricity generation, often integrated into national grids or used for standalone systems.
Components of a Solar Power Plant
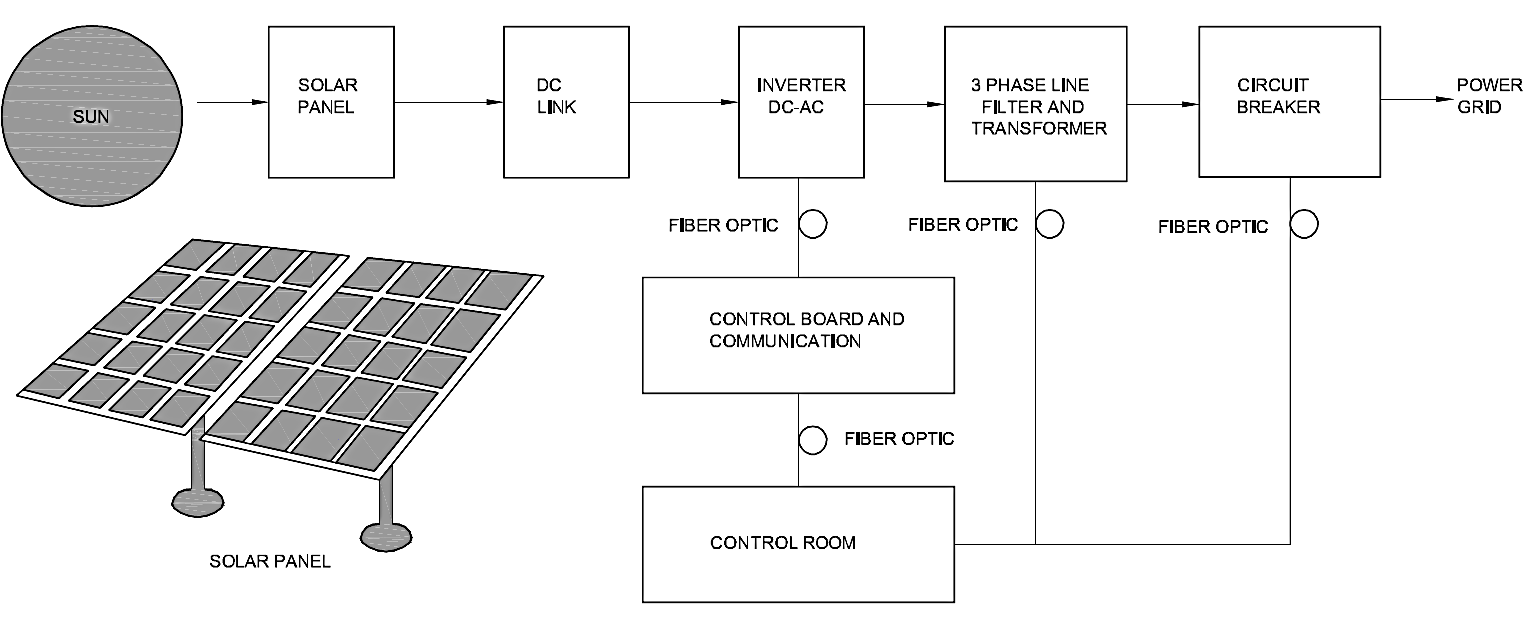
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Solar Panels | Convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity using photovoltaic cells. |
| DC Link | Stabilizes DC power output before sending it to the inverter for conversion. |
| Inverter | Converts DC electricity from solar panels into alternating current (AC) for grid compatibility. |
| Transformer | Steps up the AC voltage to meet the power grid’s requirements for efficient transmission. |
| Circuit Breaker | Protects the system by isolating faulty sections and ensuring safe operation. |
| Control System | Monitors and controls the performance of the solar power plant, including communication systems. |
| Control Room | Centralized facility for monitoring and managing the plant’s operations. |
| Power Grid Connection | Connects the plant’s output to the national or local grid for electricity distribution. |
Working of a Solar Power Plant
- Sunlight Capture: Solar panels absorb sunlight and convert it into DC electricity.
- DC Link: Stabilizes the DC output and prepares it for inversion.
- Inversion: The inverter converts DC into AC electricity.
- Voltage Step-Up: Transformers step up the AC voltage for grid compatibility.
- Transmission: Electricity flows through circuit breakers into the power grid for distribution.
Types of Solar Power Plants
| Type | Description | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Photovoltaic (PV) Power Plants | Convert sunlight directly into electricity using solar panels. | – Common for utility and rooftop systems – Monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels |
| Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) Plants | Use mirrors to concentrate sunlight, generating steam to drive turbines. | – High efficiency in sunny regions – Examples: Solar towers, parabolic troughs |
| Hybrid Solar Power Plants | Combine solar energy with other sources like wind or biomass for stable output. | – Consistent power generation – Ideal for overcoming solar variability |
| Floating Solar Power Plants | Installed on water bodies to conserve land and reduce evaporation. | – Increased efficiency due to cooling from water – Useful for reservoirs and lakes |
| Off-Grid Solar Power Plants | Designed for standalone systems without grid connection. | – Ideal for rural areas – Requires battery storage |
Advantages of Solar Power Plants
- Environmentally Friendly: Zero greenhouse gas emissions during operation.
- Renewable Energy Source: Unlimited availability of sunlight.
- Cost Savings: Reduces electricity bills over time.
- Low Maintenance: Solar panels and equipment have long lifespans.
- Energy Independence: Reduces reliance on imported fossil fuels.
- Versatile Applications: Can be deployed in remote areas or integrated into urban grids.
Disadvantages of Solar Power Plants
- Weather Dependency: Output varies based on sunlight availability (e.g., cloudy days or night).
- High Initial Costs: Installation and infrastructure require significant investment.
- Land Use: Large-scale plants require extensive land, impacting ecosystems.
- Energy Storage: Batteries for storage are costly and have limited capacity.
- Efficiency Challenges: Solar panels have conversion efficiency limitations (15-25% typically).
Applications of Solar Power Plants
- Utility-Scale Power Generation: Provides electricity to national grids.
- Rural Electrification: Supplies energy to remote areas without grid access.
- Industrial Use: Powers factories, data centers, and commercial buildings.
- Residential Use: Rooftop solar systems for homes and apartments.
- Agriculture: Solar water pumps and irrigation systems.
- Transport: Powers solar-powered electric vehicles and charging stations.
Conclusion
A solar power plant is a vital contributor to sustainable development, offering a clean and renewable energy source for diverse applications. With advancements in technology, such plants are becoming more efficient and accessible, aiding the global transition toward carbon neutrality.