A solar car is a vehicle powered entirely or partially by solar energy, utilizing photovoltaic (PV) cells to convert sunlight into electrical energy. This energy is stored in batteries and used to run an electric motor that drives the vehicle. Solar cars are designed to be lightweight, energy-efficient, and environmentally friendly. They represent a significant innovation in sustainable transportation, reducing dependence on fossil fuels while minimizing carbon emissions.
Components of a Solar Car
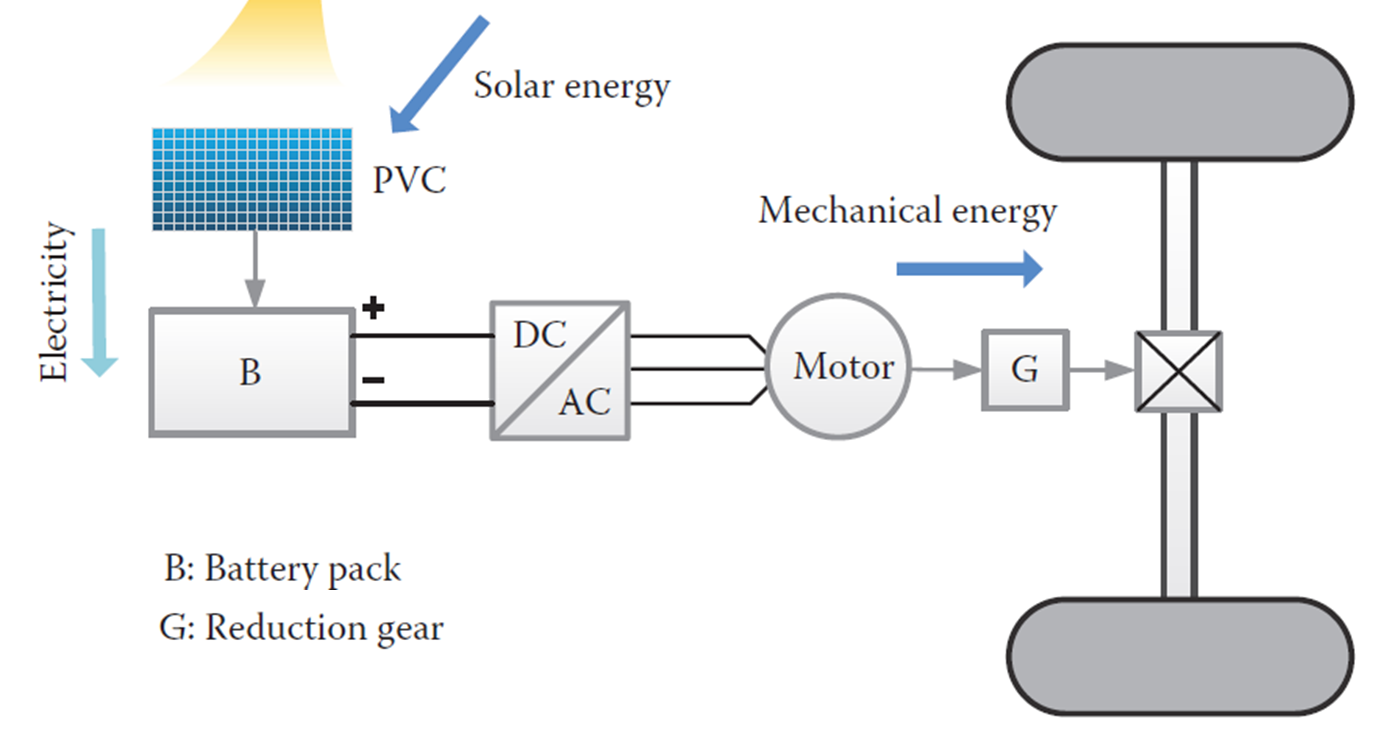
A solar car comprises several crucial components that work together to harness, store, and utilize solar energy for propulsion. Below are the main components of a solar car:
- Photovoltaic Cells (Solar Panels): PV cells are the primary energy source for solar cars. These panels capture sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity through the photovoltaic effect. Typically made of materials like silicon, they are mounted on the car’s surface to maximize sunlight absorption.
- Battery Pack (B): The battery stores the electrical energy generated by the PV cells. This energy is later used to power the electric motor, especially when sunlight is insufficient or during nighttime. Lithium-ion batteries are commonly used due to their high energy density, lightweight, and long lifespan.
- Inverter (DC to AC): Converts the DC electricity produced by the solar panels or stored in the batteries into alternating current (AC) required by the electric motor. Ensures compatibility with AC motors and enhances energy efficiency.
- Electric Motor: The motor is responsible for converting electrical energy into mechanical energy to drive the vehicle’s wheels. Common types include brushless DC motors (BLDC) or AC induction motors for their efficiency and reliability.
- Reduction Gear (G): The reduction gear optimizes the torque and rotational speed delivered by the motor, ensuring smooth and efficient propulsion. Adapts the motor’s output to suit the vehicle’s requirements.
- Energy Management System (EMS) The EMS oversees energy flow between the solar panels, battery, and motor. It ensures efficient use of energy while protecting the battery from overcharging or deep discharging. Includes monitoring systems to track energy production, consumption, and storage.
- Chassis and Aerodynamic Design: The car’s frame is built to be lightweight yet sturdy. Aerodynamic designs minimize air resistance, enhancing energy efficiency. Often constructed using lightweight composites like carbon fiber or aluminum.
- Auxiliary Components: Include lighting, brakes, steering systems, and sensors for monitoring vehicle performance.
- Sensors: Track parameters like speed, battery status, and solar panel efficiency.
Advantages of Solar Cars
Solar cars provide numerous benefits, contributing to sustainability, energy efficiency, and technological innovation. Below are the primary advantages:
- Environmentally Friendly: Solar cars produce zero emissions during operation, significantly reducing their environmental impact compared to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles.
- Renewable Energy Source: They utilize sunlight, an abundant and renewable energy source, reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
- Cost Efficiency: Minimal operating costs since sunlight is free. Maintenance costs are also lower due to fewer moving parts in electric drivetrains.
- Reduced Noise Pollution: Electric motors operate quietly, minimizing noise pollution and enhancing urban living conditions.
- Energy Independence: Solar cars provide an alternative to conventional fuels, promoting energy independence and reducing vulnerability to fuel price fluctuations.
- Technological Advancement: Drives innovation in solar technology, energy storage systems, and automotive design, benefiting other industries.
- Sustainable Transportation: Solar cars contribute to long-term sustainability by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and conserving finite resources.
Disadvantages of Solar Cars
Despite their advantages, solar cars face several challenges that limit their widespread adoption. Key disadvantages include:
- High Initial Cost: Solar cars are expensive to produce due to advanced technologies like photovoltaic cells, lightweight materials, and high-performance batteries.
- Limited Range and Speed: Performance depends on sunlight availability. Cloudy weather or nighttime operation reduces efficiency and range.
- Energy Storage Limitations: Batteries have limited storage capacities, requiring frequent recharges during long trips.
- Slow Charging: Recharging from solar panels alone can be slow, necessitating supplemental charging methods for practicality.
- Complex Design: The integration of solar panels, batteries, and other components demands advanced engineering and specialized manufacturing processes.
- Weather Dependence: Performance is heavily reliant on weather conditions. Poor sunlight availability can severely impact energy production.
- Limited Load Capacity: Lightweight materials and designs limit the cargo-carrying capacity of solar cars compared to conventional vehicles.
- Maintenance Challenges: PV cells and batteries require regular maintenance to maintain efficiency, and repairs can be costly.
Applications of Solar Cars
Solar cars have diverse applications across various sectors, demonstrating their potential as a sustainable transportation solution. Common applications include:
- Personal Transportation: Solar cars offer an eco-friendly alternative for daily commutes, reducing fuel costs and environmental impact.
- Research and Development: Frequently used in academic and industrial research to test and advance solar and automotive technologies.
- Racing and Competitions: Solar car races, such as the World Solar Challenge, showcase advancements in solar technology and promote innovation.
- Commercial Use: Ideal for last-mile delivery services, especially in sunny regions, reducing operational costs and emissions.
- Educational Tools: Solar cars are used as teaching aids in universities and schools to promote renewable energy education.
- Military and Remote Operations: Useful in remote areas where fuel supply is limited, as they can operate independently using sunlight.
- Tourism and Recreation: Solar-powered vehicles are employed for sightseeing tours in environmentally sensitive areas like national parks.
- Emergency Services: Solar cars equipped with battery storage can be used for essential services during power outages or in disaster-stricken areas.
- Agricultural Applications: Suitable for transporting goods and equipment on farms, especially in regions with abundant sunlight.
- Urban Mobility Solutions: As part of sustainable urban development, solar cars can complement public transportation systems by providing clean, last-mile connectivity.
Future of Solar Cars
Solar cars represent a promising frontier in sustainable transportation. As technology advances, the following developments are anticipated:
- Improved Efficiency: Enhanced photovoltaic cell efficiency will increase energy conversion rates, making solar cars more viable for everyday use.
- Better Energy Storage: Innovations in battery technology will extend range, reduce charging times, and improve overall performance.
- Cost Reductions: Mass production and advancements in materials will lower manufacturing costs, making solar cars more accessible to consumers.
- Integration with Smart Grids: Solar cars could serve as mobile energy storage units, feeding surplus electricity back into the grid.
- Widespread Adoption: As awareness of climate change and sustainability grows, solar cars are likely to gain traction among environmentally conscious consumers and businesses.
Conclusion
Solar cars symbolize the convergence of renewable energy and transportation, offering a clean and sustainable alternative to fossil fuel-based vehicles. While challenges like cost and weather dependence remain, ongoing technological advancements promise to make solar cars more practical and accessible. As societies strive toward a greener future, solar cars are poised to play a crucial role in reducing carbon footprints and fostering sustainable development.