An electric bicycle, often referred to as an e-bike, is a bicycle that is equipped with an integrated electric motor and battery system designed to assist with propulsion. E-bikes maintain the general functionality of traditional bicycles, allowing the rider to pedal and use gears, but with the added benefit of electrical assistance. The motor provides support to the rider, reducing physical effort, especially during uphill rides, against strong headwinds, or over long distances.
Components of an Electric Bicycle
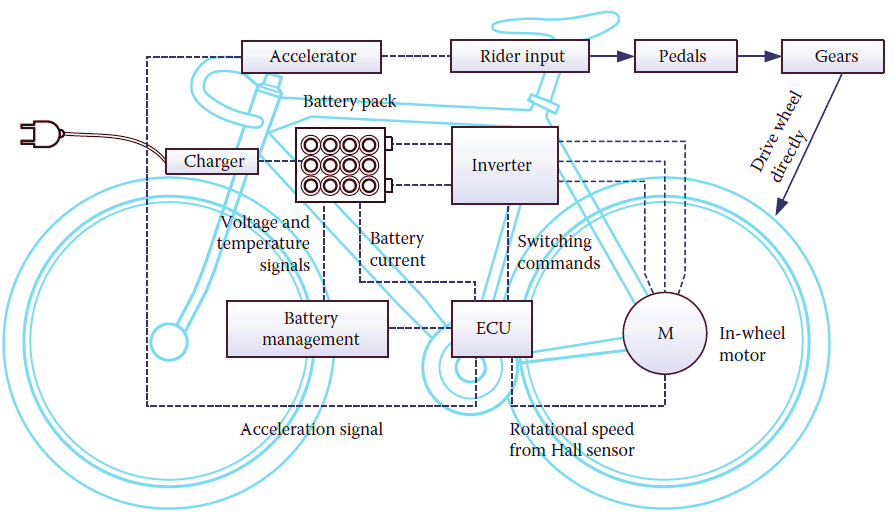
Electric bicycles are composed of several distinct components that work together to provide motorized assistance while maintaining traditional cycling capabilities. Below is an overview of the essential components:
Battery Pack: The battery is the primary energy source for the e-bike. It stores electrical energy and supplies it to the motor. Most e-bike batteries are lithium-ion types due to their high energy density, lightweight, and long lifespan. Rechargeable, varying capacities (measured in watt-hours), and typically mounted on the frame or integrated into the design.
Electric Motor: The motor is responsible for converting electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy to propel the bicycle. Common types include:
-
-
- Hub Motors: Integrated into the wheel (front or rear).
- Mid-drive Motors: Mounted near the bike’s bottom bracket for better weight distribution and efficiency.
-
Electronic Control Unit (ECU): The ECU acts as the brain of the e-bike, managing the flow of electrical power from the battery to the motor based on input from sensors and user settings. It ensures smooth operation and optimal performance.
Pedals and Gears: E-bikes retain traditional pedal and gear systems, enabling riders to pedal manually when preferred or necessary. The motor can complement pedaling by providing assistance proportional to the rider’s effort.
Charger: The charger is used to replenish the battery’s energy by connecting it to an external power source. Modern chargers often include safety features to prevent overcharging.
Inverter: Converts DC power from the battery into AC power required to drive the motor. It plays a critical role in ensuring efficient energy utilization.
Sensors: Various sensors collect data to optimize the riding experience:
- Hall Sensors: Detect the rotational speed of the motor.
- Torque Sensors: Measure the rider’s pedaling force to adjust motor assistance.
- Speed Sensors: Monitor the bike’s speed to comply with regulatory limits and adjust motor output.
Battery Management System (BMS): Protects the battery by monitoring its voltage, temperature, and current. It ensures safe charging and discharging cycles, preventing overheating or overloading.
Display and Controls: A handlebar-mounted display provides information such as speed, battery level, and assistance mode. Controls allow riders to adjust settings like motor assistance level and lighting.
Frame and Wheels: E-bike frames are often reinforced to accommodate the added weight of the motor and battery. Specialized wheels and tires may also be used for durability and better traction.
Advantages of Electric Bicycles
Electric bicycles offer a variety of benefits that make them a popular alternative to traditional bicycles and motorized vehicles:
- Environmental Benefits: Zero emissions during use, contributing to reduced air pollution and lower carbon footprint compared to cars or motorcycles.
- Cost-Efficiency: Lower operating and maintenance costs compared to fuel-powered vehicles. Electricity is generally cheaper than gasoline, and e-bikes require less frequent servicing.
- Health Benefits: Encourages physical activity, as riders can still pedal while receiving assistance. This makes e-bikes accessible to a wider range of fitness levels.
- Ease of Use: Reduces physical strain, especially for commuting, carrying cargo, or traveling uphill. Riders can arrive at their destination less fatigued.
- Accessibility: Makes cycling more accessible to people with limited mobility or those recovering from injuries.
- Traffic Avoidance: Ideal for navigating congested urban areas and taking bike lanes, reducing commute times.
- Versatility: Suitable for various applications, including commuting, recreation, and cargo transportation.
- Silent Operation: Motors are generally quiet, ensuring a pleasant and non-disruptive riding experience.
Disadvantages of Electric Bicycles
Despite their numerous advantages, e-bikes have some limitations:
- Higher Initial Cost: E-bikes are more expensive than traditional bicycles due to their advanced components like motors and batteries.
- Weight: The addition of a motor and battery makes e-bikes heavier, potentially making them harder to handle when the battery is depleted.
- Limited Range: Range is dependent on battery capacity, terrain, rider weight, and assistance level. Long trips may require frequent recharging.
- Battery Life and Replacement Costs: Batteries degrade over time and need replacement after a few years, which can be costly.
- Regulations: Legal restrictions on motor power and speed may vary across regions, requiring riders to stay informed.
- Maintenance Complexity: Additional electrical components require specialized maintenance compared to traditional bicycles.
- Charging Time: Recharging the battery can take several hours, making long-distance or frequent use less convenient without proper planning.
- Vulnerability to Theft: High-value components like batteries and motors are attractive targets for theft.
Applications of Electric Bicycles
Electric bicycles have diverse applications across various sectors:
- Personal Commuting: Ideal for short- to medium-distance commutes in urban and suburban areas, providing a cost-effective and eco-friendly alternative to cars.
- Recreational Use: Popular for leisure rides, e-bikes allow users to explore trails and scenic routes without excessive physical exertion.
- Cargo and Delivery Services: E-bikes equipped with cargo carriers are increasingly used in logistics for last-mile delivery, especially in congested cities.
- Tourism: E-bikes are rented out in tourist hotspots, enabling visitors to explore larger areas comfortably.
- Healthcare and Rehabilitation: Provides a means of low-impact exercise for individuals recovering from injuries or managing chronic conditions.
- Sports and Fitness: Used for training purposes, allowing riders to maintain steady effort levels during cycling workouts.
- Military and Emergency Services: E-bikes are employed in specific scenarios requiring quiet and efficient transportation, such as patrolling or search-and-rescue operations.
- Rural Transportation: Provides a reliable and affordable mode of transport for people in rural areas with limited access to public transportation.
- Utility and Farm Use: Adapted for use in agricultural settings, enabling workers to traverse large fields and carry tools.
Conclusion
Electric bicycles are a transformative technology bridging the gap between traditional bicycles and motorized vehicles. They offer an eco-friendly, cost-effective, and versatile transportation option for diverse user groups. Despite some limitations, the ongoing advancements in battery technology, motor efficiency, and lightweight materials continue to enhance their appeal. E-bikes are not only shaping the future of urban mobility but also contributing to a healthier, more sustainable world.