Energy-efficient motors are advanced electric motors designed to utilize electrical energy more effectively, reducing energy losses caused by heat, friction, and inefficiencies. These motors meet or exceed international efficiency standards, such as NEMA Premium and IEC standards, ensuring optimized performance and minimal energy consumption.
Characteristics of Energy-Efficient Motors
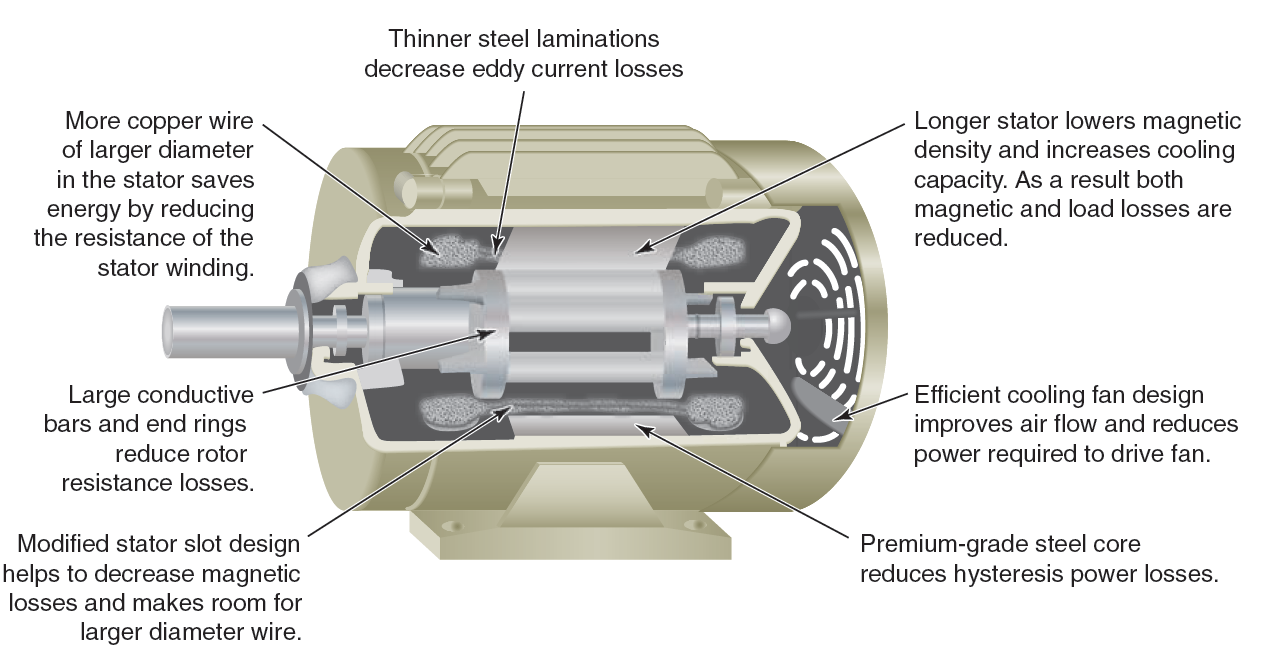
- Reduced Power Losses: Utilize premium-grade materials to minimize losses such as eddy current and hysteresis losses.
- High-Quality Design: Improved winding designs and thinner steel laminations for higher efficiency.
- Enhanced Cooling Systems: Efficient fans and better heat dissipation mechanisms to reduce thermal losses.
- Durable Construction: Designed with robust materials for long operational life and low maintenance.
- Optimized Rotor and Stator: Larger conductive bars and reduced air gaps for better magnetic performance.
Difference Between Energy Efficient Motor and Standard Motor
| Feature | Energy Efficient Motor | Standard Motor |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Consumption | Lower | Higher |
| Initial Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Operational Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Lifespan | Longer | Shorter |
| Efficiency | High | Moderate |
Advantages of Energy-Efficient Motors
- Energy Savings: Consume less electricity compared to conventional motors, reducing energy bills.
- Environmental Benefits: Lower carbon footprint due to reduced energy consumption.
- Enhanced Lifespan: Operate at lower temperatures, reducing wear and tear.
- High Reliability: Minimal downtime due to robust and durable components.
- Compliance with Standards: Meet global energy efficiency regulations and certifications.
Disadvantages of Energy-Efficient Motors
- High Initial Cost: More expensive to purchase compared to standard motors.
- Limited Availability: May not be available in all power ratings or regions.
- Specialized Maintenance: May require trained personnel for repair and servicing.
- Weight and Size: Slightly heavier due to additional design features like improved insulation.
Applications of Energy-Efficient Motors
- Industrial Use: Pumps, compressors, conveyors, and industrial machines.
- Commercial Buildings: HVAC systems, elevators, and escalators.
- Agriculture: Irrigation systems and agricultural machinery.
- Renewable Energy Systems: Wind turbines and solar-powered setups.
- Transportation: Electric vehicles and hybrid systems.