A pole mounted substation is a type of outdoor substation used for distributing power in low-voltage systems. It is typically mounted on a pole structure and is designed to step down the high-voltage (HV) electricity from the transmission or distribution line to a lower voltage (LV) suitable for end-users, such as residential or small industrial loads. These substations are commonly used in rural or semi-urban areas due to their cost-effectiveness and simplicity.
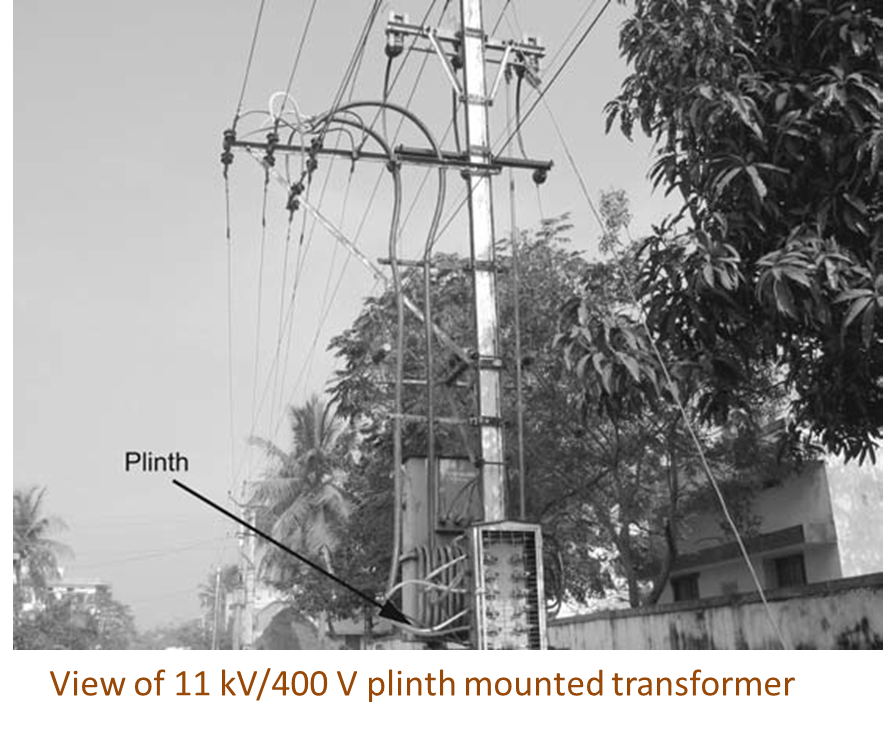

What is Pole Mounted Substation?
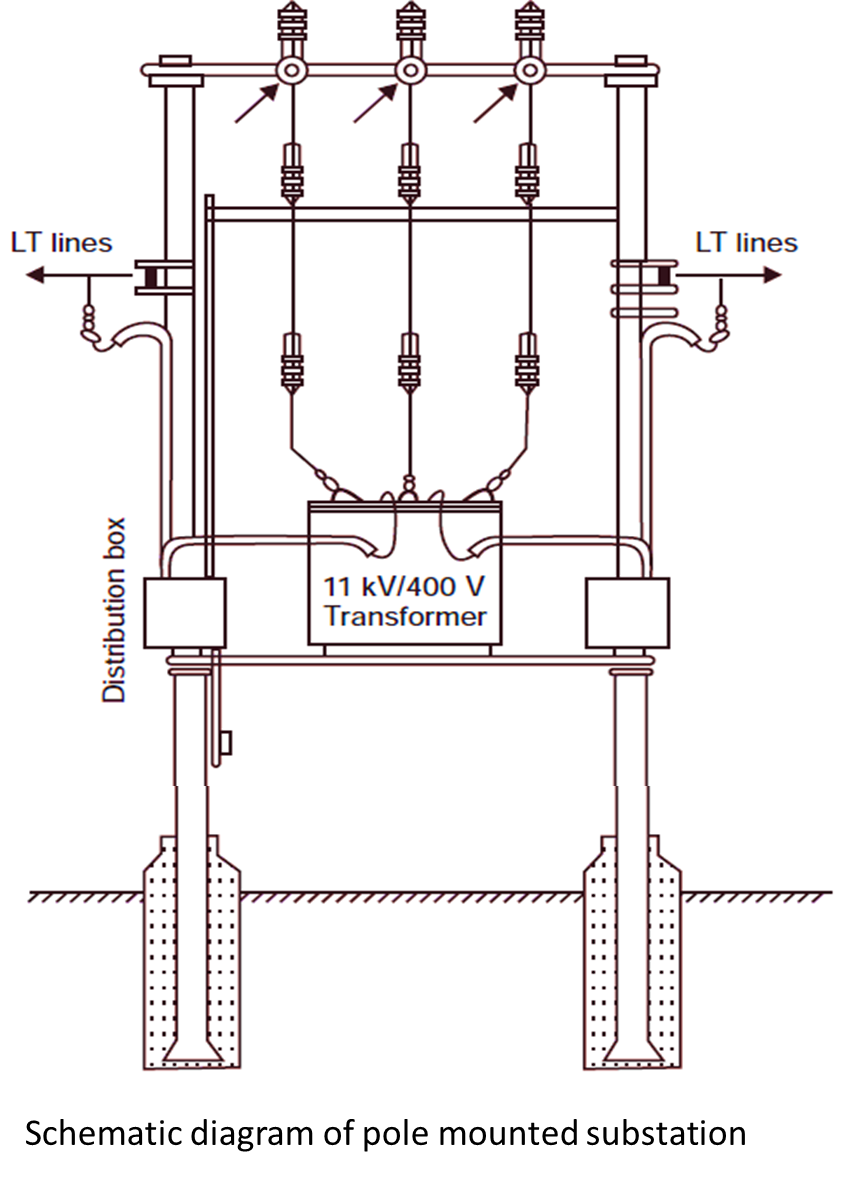
A pole-mounted substation is an outdoor distribution substation mounted on a pole. It steps down high voltage (usually 11 kV) to low voltage (400 V or 230 V) for distribution to residential, commercial, or agricultural loads.
Components of a Pole Mounted Substation
- High Tension (HT) Incoming Line: Connects the substation to the high-voltage distribution network.
- Lightning Arresters: Protect the substation equipment from voltage surges caused by lightning strikes or switching operations.
- Circuit Breaker (CB) or Switch: Disconnects the incoming line during faults or for maintenance.
- HG (High Grade) Fuse: Protects the transformer from overcurrent or short circuits.
- Distribution Transformer: Steps down the voltage from 11 kV to 400 V or 230 V.
- Low Tension (LT) Fuse: Provides additional protection for outgoing low-voltage lines.
- LT Lines: Distribute the stepped-down voltage to the end users.
Single Line Diagram (SLD) of Pole Mounted Substation
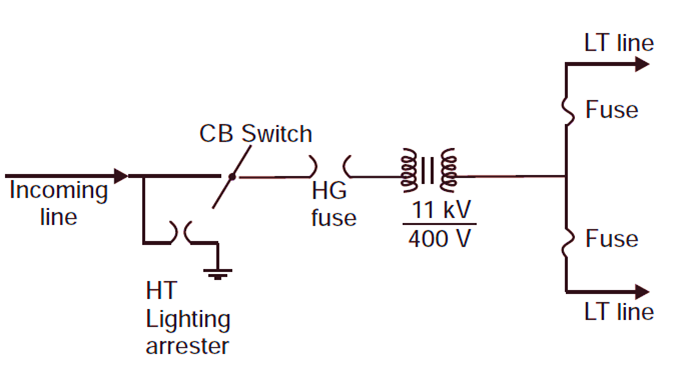
The single line diagram simplifies the representation of electrical components and their connections in the substation.
- Incoming Line: Represents the high-voltage input (11 kV) from the grid.
- Lightning Arrester: Connected to ground to divert high-voltage surges to the earth.
- CB or Switch: Isolates the substation for operational safety during faults or maintenance.
- HG Fuse: Provides protection to the transformer by disconnecting it during faults or overcurrent.
- Transformer: Steps down the voltage from 11 kV to 400 V.
- LT Fuse: Protects the low-voltage distribution lines from overcurrent or short circuits.
- LT Lines: Deliver power to the consumers at 400 V or 230 V.
Advantages of Pole Mounted Substation
- Cost-Effective: Requires minimal infrastructure and materials, making it cheaper than ground or indoor substations.
- Compact Design: Takes up less space as the equipment is mounted on a pole, making it suitable for areas with space constraints.
- Quick Installation: Easy to install and requires less time compared to conventional substations.
- Ease of Maintenance: The simple layout and elevated structure make it easy to inspect and maintain.
- Reliable for Small Loads: Ideal for small-scale power distribution in rural or semi-urban areas.
- Reduced Land Use: No need for large land areas, reducing land acquisition costs.
- Good for Distributed Loads: Efficient for supplying scattered consumers like rural households or farms.
Disadvantages of Pole Mounted Substation
- Limited Capacity: Suitable only for small loads (usually up to 200 kVA), making it unsuitable for large industrial or urban loads.
- Vulnerability to Weather Conditions: Exposed to environmental factors like storms, lightning, and rain, which may cause outages or equipment damage.
- Safety Risks: Equipment is mounted on poles, posing risks if components fall or if unauthorized persons access it.
- Shorter Lifespan: The outdoor exposure may reduce the lifespan of some components.
- Limited Expansion: Scaling up capacity or modifying the setup can be challenging.
- Prone to Overloading: Due to the small capacity, it may face overloading issues in areas with rapid demand growth.
- Noise Concerns: Transformers mounted on poles may produce noise, which can disturb nearby residents.
Applications of Pole Mounted Substation
- Rural Electrification: Provides power to remote and sparsely populated areas where small loads need to be distributed over a wide area.
- Agricultural Loads: Supplies power for irrigation pumps, water lifting, and other farming equipment.
- Residential Areas: Serves small housing clusters, villages, or individual homes in semi-urban or rural regions.
- Street Lighting: Supplies power for street lights in rural or semi-urban areas.
- Temporary Power Supplies: Used for temporary applications, such as powering construction sites or special events.
- Small Commercial Loads: Supplies power to small businesses or shops in less dense areas.
Key Features of a Pole Mounted Substation
- Compact Design: The equipment is mounted on poles, making it space-efficient.
- Voltage Levels: Generally used for stepping down electricity from 11 kV to 400 V or 230 V.
- Low Cost: These substations are economical compared to ground-based or indoor substations.
- Ease of Maintenance: Simple design and easy accessibility for routine maintenance.
Conclusion
Pole-mounted substations are an essential component of the distribution system, particularly in rural and semi-urban areas. Their cost-effectiveness and simplicity make them suitable for smaller loads, although they come with limitations like reduced capacity and exposure to environmental risks. For applications where space and cost are constraints, they provide an efficient solution.
Related Posts
- Working Principle of Single Phase Induction Motor
When a single-phase induction motor is supplied from a source, the flux produced will be…
- Single Phase Half Wave Controlled Rectifier
In Single Phase Half Wave Controlled Rectifiers the load power can be controlled in only…
- What is Shaded Pole Induction Motor? Working Principle, Diagram & Applications
Shaded pole induction motor is more or less similar to single-phase induction motor. The stator…
- What is Single Phase Induction Motor? Construction, Parts, Diagram & Applications
Characteristics of Single Phase Induction Motor The following are the inherent characteristics of single phase…
- What is Star Connection (Y Connection)? Phasor Diagram, Formula, Line & Phase (Voltage and Current)
Figure 1. Star Connection (Y Connection) is obtained by connecting one end of the three…