A solar cooker is a device that harnesses solar energy (sunlight) to cook food. It is an environmentally friendly alternative to conventional cooking methods as it eliminates the use of non-renewable energy sources such as wood, gas, or electricity. Solar cookers work on the principle of converting sunlight into heat energy, which is then utilized to cook meals or heat liquids.
Components of a Solar Cooker
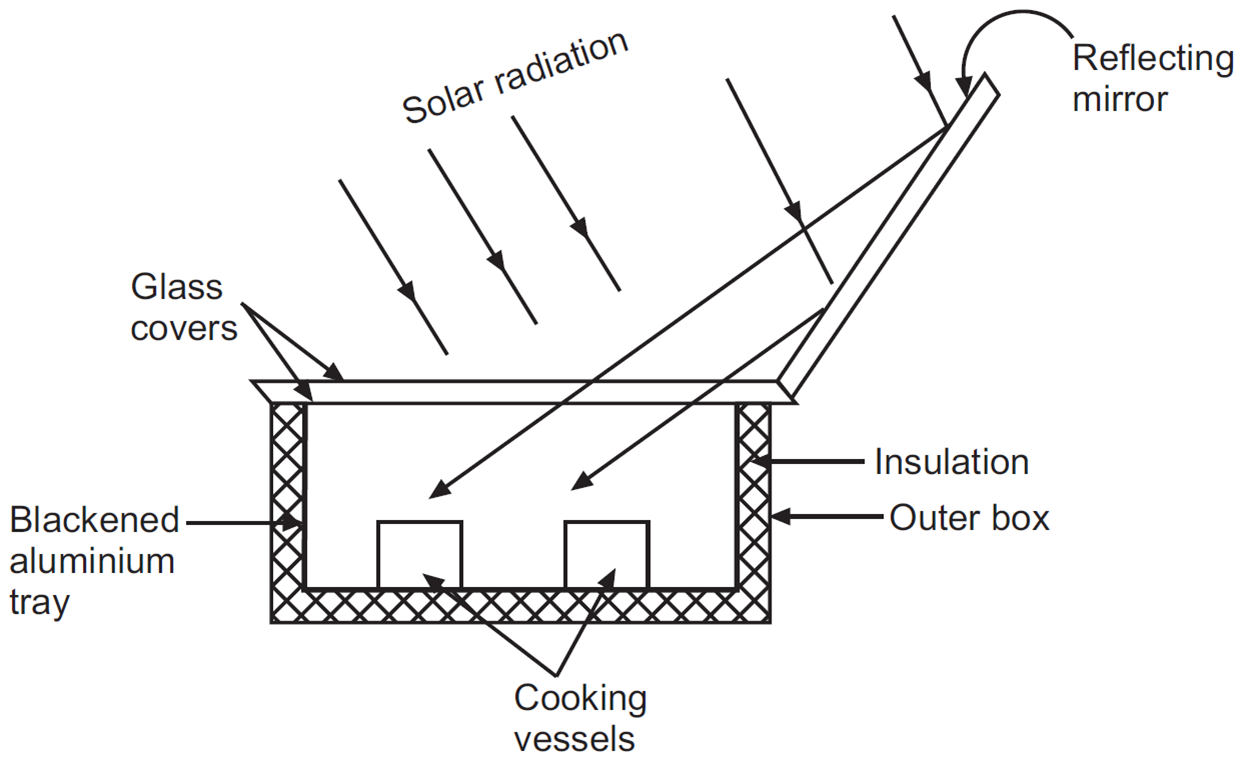
Figure 1: Solar Cooker.
A solar cooker typically consists of the following components:
- Outer Box: The outer casing that provides structural support to the cooker. It is made of durable materials and often insulated to prevent heat loss.
- Insulation: A layer of insulating material is added between the outer box and the cooking area to minimize heat loss. Materials like wool, thermocol, or polyurethane foam are commonly used.
- Glass Cover(s): Transparent glass or plastic sheets are placed over the cooking chamber to trap heat through the greenhouse effect.
- Blackened Aluminum Tray: A metal tray painted black to maximize heat absorption. The black surface helps convert sunlight into heat more efficiently.
- Reflecting Mirror: A reflective surface, usually made of polished aluminum or a mirror, directs additional sunlight into the cooking chamber, increasing the temperature inside.
- Cooking Vessels: Dark-colored vessels are preferred as they absorb heat better. These vessels are placed inside the cooker to hold the food being cooked.
Working Principle of a Solar Cooker
The working of a solar cooker is based on three fundamental principles: reflection, absorption, and retention.
- Reflection: The reflective mirror captures sunlight and redirects it into the cooker’s interior. This increases the concentration of sunlight and boosts the cooking temperature.
- Absorption: The blackened surfaces (tray and cooking vessels) absorb the concentrated sunlight and convert it into heat energy.
- Retention: The glass cover traps the heat inside the cooker, minimizing heat loss through the greenhouse effect. Insulation further ensures that the heat remains within the cooking chamber.
Types of Solar Cookers
Solar cookers are categorized into the following types based on their design and functionality:
| Type | Description | Advantages | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Box-Type Solar Cooker | A common design with a rectangular or square box, suitable for slow cooking and baking. | Simple to use and affordable. | Domestic use for baking and slow cooking. |
| Parabolic Solar Cooker | Uses a parabolic reflector to focus sunlight onto a single point, achieving higher temperatures. | Ideal for frying and high-heat cooking. | Commercial and domestic use. |
| Panel Solar Cooker | Consists of flat reflective panels that direct sunlight onto a cooking pot. | Lightweight and portable. | Camping and outdoor cooking. |
| Vacuum Tube Solar Cooker | Utilizes evacuated tubes to trap heat and cook food efficiently, even in colder climates. | High efficiency and works in cold weather. | Rural and remote areas. |
Advantages of Solar Cookers
- Environmentally Friendly: Solar cookers rely solely on renewable solar energy, reducing carbon emissions.
- Cost-Effective: No fuel is required, leading to significant savings on energy costs.
- Health Benefits: Eliminates indoor air pollution caused by burning wood or charcoal.
- Energy Independence: Reduces dependence on non-renewable energy sources like gas or electricity.
- Ease of Use: Requires minimal maintenance and has no recurring operational costs.
- Portable: Lightweight designs can be transported easily for outdoor use.
Disadvantages of Solar Cookers
- Weather Dependency: Cannot be used during cloudy or rainy days.
- Longer Cooking Time: Cooking may take more time compared to conventional methods.
- Limited High-Temperature Cooking: May not be suitable for frying or other high-temperature cooking techniques.
- Initial Cost: Some advanced models may have a higher initial investment.
- Inconvenience: Requires frequent adjustment to track the sun’s movement.
Applications of Solar Cookers
- Domestic Cooking: Ideal for households in sunny regions to prepare daily meals.
- Outdoor Cooking: Useful for camping, picnics, and other outdoor activities.
- Disaster Relief: Provides a reliable cooking solution in areas without access to conventional energy sources.
- Educational Tool: Demonstrates the practical application of solar energy in schools and universities.
- Community Kitchens: Large-scale solar cookers can be used in community kitchens to serve meals efficiently.
- Sustainable Development: Promotes the use of renewable energy in rural and remote areas.
Conclusion
Solar cookers are a remarkable innovation that demonstrates the potential of renewable energy. By leveraging sunlight, they provide an eco-friendly, cost-effective, and sustainable solution for cooking. Despite some limitations, advancements in solar cooker designs continue to enhance their efficiency and usability, making them a valuable tool in the transition to a greener future. The widespread adoption of solar cookers can significantly reduce our carbon footprint and promote energy independence while addressing global challenges like deforestation and energy poverty.