Characteristics of Single Phase Induction Motor
The following are the inherent characteristics of single phase induction motor.
- There is no starting torque in this motor.
- If the motor is made to rotate by any means, the motor picks up the speed and continues to rotate in the same direction developing the operating torque.
Construction of Single Phase Induction Motor
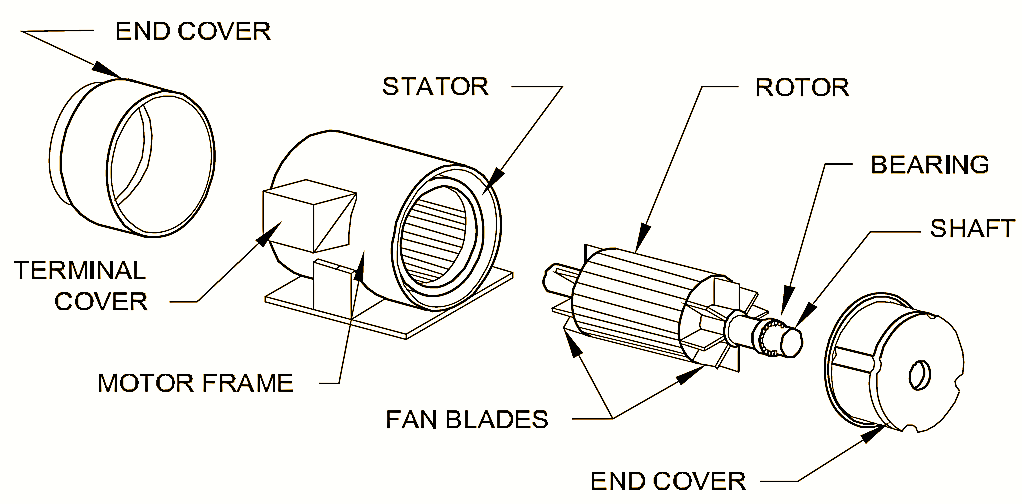
Figure 1.
The single-phase induction motor mainly consists of two parts. They are as follows,
- Stator
- Rotor.
1. Stator
The stator is a stationary hollow cylindrical structure and it is the outer covering of the motor. The stator core is usually made up of cast iron or cast steel. A large number of axial slots are cut around the inner periphery of the core and these slots shelter the stator conductors. The stator winding of a single-phase induction motor is provided with concentric coils as shown in figure (1). The most widely used number of poles in the induction motor are 2, 4, 6, so that the induction motor can be wound for even number of poles. Practically, each coil has a number of turns but for convenience, only one turn of the coil is shown in figure (l). The stator core is made up of laminations which are usually 0.036 to 0.06 cm thick. Generally, the motors consisting of squirrel cage type are provided with 2 stator windings (except for the shaded pole motor). Both the windings are identical to that as shown in figure (l). Among these, one of the stator winding is provided with the heaviest wire, and these 2 stator windings are arranged in such a way that they are in space quadrature with respect to each other. In the motor which works with both the windings energized, the winding with much thin wire is known as auxiliary winding and the other is called as the main winding.
2. Rotor
It is the part of the motor that develops the driving torque and rotates. In practice there are two types of rotors, and the choice of the rotor is made on the basis of the application for which the motor is employed. The two types of rotor are,
- Squirrel cage rotor
- Slip ring rotor.
(i) Squirrel Cage Rotor: The rotor core is cylindrical and is usually made of cast iron or cast steel. All along the periphery of the core, longitudinal slots are made and these slots are embedded rotor conductors. The rotor conductors are usually thick bars of copper or aluminium. They are permanently welded to two copper end lings as shown in figure (2).
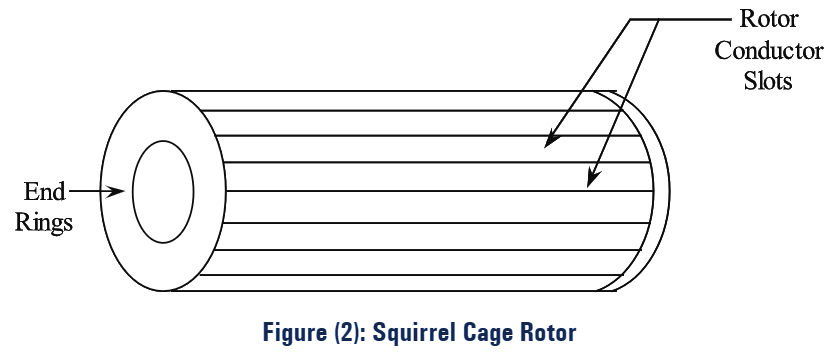
By this arrangement, the rotor always forms a closed-circuit. This type of construction is termed as squirrel cage construction.
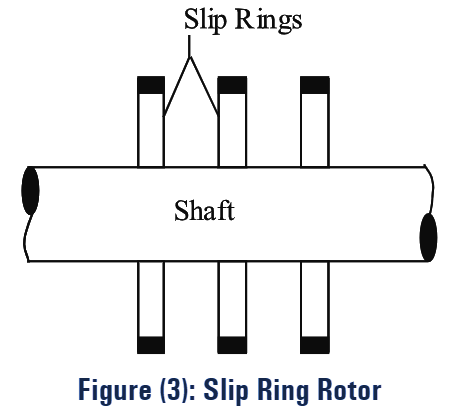
(ii) Slip Ring Rotor: The rotor core is cylindrical. Slots are cut around the periphery of the core, and these slots house the rotor windings. The rotor conductors are in the form of copper wire. The slip rings of the rotor are shown in figure (3).
Applications of single phase induction motor
Ans: Single phase induction motors find their applications in,
- Fans
- Refrigerators
- Vacuum cleaners
- Centrifugal pump
- Machine tools
- Blowers
- Washing machines
- Grinders
- Compressors
- Conveyors.
Q1. What are the disadvantages of a single phase induction motor when compared with a 3-phase induction motor?
Ans: The following are the disadvantages of single phase induction motor when compared with 3-phase induction motor.
- Single phase induction motors are not self-starting, whereas 3-phase induction motors are self starting.
- The power factor of single phase induction motors is lower than 3 -phase induction motors.
- Single phase induction motors have lower efficiency than 3-phase motors.
- For the same rating, the output of single phase induction motor is half that of 3-phase induction motors.
- For the same output, single phase motors are costlier than 3-phase motors.
Q2. Why a single phase induction motor needs an auxiliary winding?
Ans:
Single phase induction motor needs an auxiliary winding because of the following reasons.
- To establish a rotation in magnetic field of stator because the main winding alone cannot establish a rotating magnetic field.
- To predetermine the direction of rotation of motor.
Q3. How is the direction of rotation of a single phase induction motor reversed?
Ans: The direction of rotation of a single phase induction motor can be reversed by reversing the connections of start winding without disturbing the connections of run winding and vice-versa. Hence, the direction of a single phase induction motor can be reversed by reversing the connections of either start or run winding but not both at the same time.
Q4. Why single phase induction motor is not self starting? Mention any one method of starting.
Ans: Whenever the stator windings of a single phase induction motor are excited by a single phase A.C supply, an alternating flux is produced in the rotor which has the same axis to that of the stator. The rotor flux tries to oppose the main field flux.
Due to the lack of relative motion between the stator and rotor fluxes, the rotor fails to rotate resulting in no torque. Hence the single phase induction motor is not self starting. There are different methods to start induction motor, split phase method is one among them.
Q5. What are the various methods available for making a single-phase motor self-starting?
Ans: The various methods used for starting of single phase induction motor are,
- Split phase method
- Capacitor start method
- Capacitor run method
- Shaded pole method.
Q6. Name the motor being used in ceiling fans.
Ans: Single phase induction motor with split phase is used in ceiling fans due to its smooth torque-speed characteristics and ability to run very efficiently at constant speed.