A Ring Main Distribution System is a closed-loop configuration of electrical distribution, where the power supply forms a ring. This system allows the power to flow in either direction to serve loads, ensuring reliability and flexibility in power distribution.
What is Ring Main Distribution System?
In this configuration:
- A ring is formed by connecting multiple distribution points or transformers.
- Circuit breakers and switches are strategically placed to isolate faults and maintain service to unaffected areas.
- The system connects the load points through feeders in a loop from a single substation or between two substations.
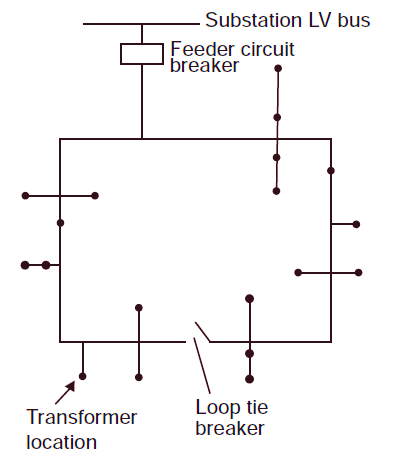
Figure 1.
The figure 1 illustrates a typical Ring Main Distribution System:
- Substation LV Bus: Supplies power to the distribution system.
- Feeder Circuit Breaker: Protects the outgoing feeders from the substation.
- Transformer Location: Transformers step down voltage for local loads.
- Loop Tie Breaker: Connects or isolates sections of the ring, improving reliability and enabling maintenance without disrupting the entire system.
Advantages of Ring Main Distribution System
- High Reliability: Faults can be isolated without affecting the entire system. The power can be supplied from either direction, ensuring continuity of service.
- Flexibility in Operation: Maintenance can be performed on one section while keeping the rest of the system operational. The load can be redistributed during peak hours by switching the loop tie breaker.
- Voltage Stability: The closed-loop configuration reduces voltage drops across the system.
- Scalability: Easy to expand the system by adding more load points or transformers without major reconfiguration.
- Efficient Fault Management: Faults can be detected and isolated quickly due to sectionalized protection devices.
- Improved Power Quality: Balances the load and reduces losses by using both sides of the ring.
Disadvantages of Ring Main Distribution System
- High Initial Cost: Requires additional cables, switches, and circuit breakers compared to radial systems.
- Complex Design and Maintenance: Requires careful planning of protection schemes and switching devices. The fault detection and restoration can be challenging due to the closed-loop nature.
- Protection Challenges: Coordinating protective devices is complex due to bidirectional power flow.
- Expensive Equipment: Loop tie breakers, relays, and other devices increase the overall cost.
- Risk of Cascading Failures: In the event of multiple faults, the system may lose redundancy and affect reliability.
Applications of Ring Main Distribution System
- Urban Distribution Systems: Widely used in cities where reliability and continuity of power are critical.
- Industrial Areas: Ensures uninterrupted power supply for industries with sensitive equipment.
- Commercial Complexes: Reduces downtime and ensures continuous power to critical facilities like malls and office buildings.
- Healthcare Facilities: Hospitals and medical centers benefit from the redundancy and reliability of the system.
- Educational Campuses: Large campuses with multiple buildings and laboratories use ring mains for stable power distribution.
- Transportation Networks: Used in railway power supply and airport distribution systems for ensuring operational continuity.
Difference between Radial Distribution System and Ring Main Distribution System
| Aspect | Ring Main System | Radial System |
|---|---|---|
| Reliability | High (faults can be isolated) | Low (fault disrupts downstream loads) |
| Cost | Higher (more equipment) | Lower |
| Fault Restoration | Faster (multiple paths for power) | Slower |
| Voltage Regulation | Better (less voltage drop) | Poorer |
| Flexibility | High | Low |
| Protection Complexity | Higher | Lower |
Protection in Ring Main Distribution System
Effective protection is critical for ensuring reliability in a ring main system. Key components of the protection scheme include:
- Circuit Breakers: Installed at the substations and strategic points in the ring to isolate faulty sections.
- Relays: Overcurrent relays and directional relays are used to detect and isolate faults.
- Automatic Reclosers: Automatically restore power after clearing temporary faults.
- Sectionalizers: Work with reclosers to isolate faulty sections without disrupting the entire ring.
- Fuses: Provide localized protection for transformers and lateral branches.
- SCADA Systems: Allow remote monitoring and control of switches, enabling quick fault isolation and restoration.