An on grid solar inverter is a key component in solar power systems that are connected to the main power grid. Its primary function is to convert the direct current (DC) electricity generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is compatible with the utility grid. On-grid systems do not require battery storage and rely on the grid to balance supply and demand.
Components of an On-Grid Solar Inverter
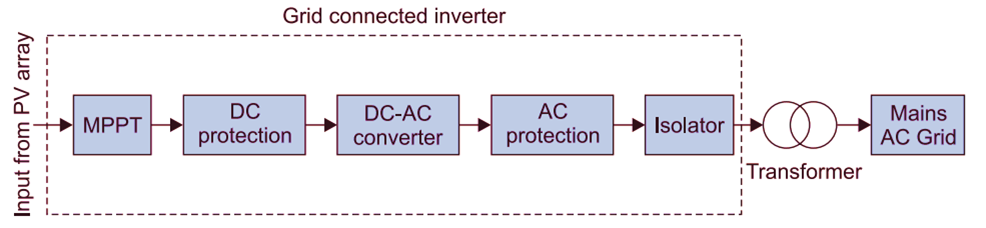
- Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT): Ensures that the solar panels operate at their maximum power output under varying conditions such as sunlight intensity and temperature.
- DC Protection: Provides safeguards against electrical faults on the direct current side, such as overvoltage, reverse polarity, or short circuits.
- DC-AC Converter: Converts the direct current (DC) from the solar panels into alternating current (AC) suitable for grid supply.
- AC Protection: Protects the system from faults on the alternating current side, including overcurrent and grid fluctuations.
- Isolator: Disconnects the inverter from the grid during maintenance or emergencies to ensure safety.
- Transformer: Steps up or down the voltage level of the electricity to match the grid’s requirements.
- Grid Connection Point: Links the solar system to the main utility grid.
Step by Step Working of On Grid Solar Inverter
- Solar Energy Collection: Solar panels absorb sunlight and convert it into DC electricity.
- MPPT Operation: The MPPT controller adjusts the voltage and current to extract the maximum power from the solar panels.
- DC to AC Conversion: The inverter transforms the DC power into AC power compatible with grid standards (e.g., 230V, 50Hz or 110V, 60Hz).
- Synchronization with Grid: The inverter synchronizes the frequency and phase of the AC power with the grid to ensure seamless integration.
- Energy Export: If the solar system generates excess electricity, it is exported to the grid, earning credits in systems like net metering.
Advantages of On Grid Solar Inverters
- Cost-Effective: Eliminates the need for expensive battery storage systems.
- Grid Backup: Provides access to the grid for electricity during nighttime or cloudy days.
- Energy Efficiency: Achieves higher efficiency compared to off-grid systems due to fewer energy losses.
- Net Metering Benefits: Allows users to earn credits for excess energy sent to the grid, reducing electricity bills.
- Scalability: Suitable for small residential systems to large-scale commercial installations.
Disadvantages of On Grid Solar Inverters
- Grid Dependency: The system stops functioning during a grid outage, as it relies on the grid for synchronization.
- No Backup Power: Unlike off-grid systems, it cannot store electricity for later use.
- Voltage and Frequency Fluctuations: Susceptible to grid-related issues, which may affect inverter performance.
- Initial Investment: High upfront cost for installation and integration with the grid.
Applications of On Grid Solar Inverters
- Residential Solar Systems: Powering homes and reducing dependency on utility power.
- Commercial Buildings: Supporting energy needs for offices, shopping malls, and industries.
- Utility-Scale Solar Farms: Feeding large quantities of solar electricity into the grid.
- Educational Institutions: Reducing energy costs in schools and universities.
- Public Infrastructure: Powering streetlights, traffic signals, and public utilities.