A Kit Kat fuse is a simple, reusable fuse primarily used for low and medium-voltage applications. It consists of a porcelain base and a fuse carrier that holds the fuse element. Kit Kat fuses are commonly used in domestic, industrial, and agricultural electrical installations for overcurrent protection.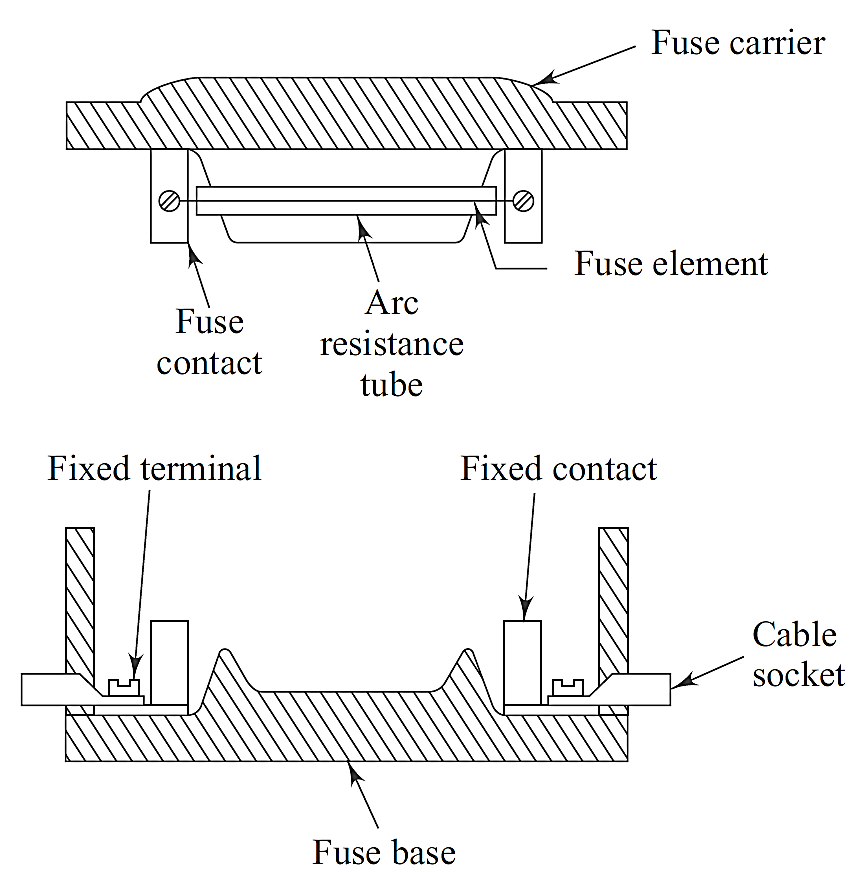
Figure 1: Kit Kat Fuse.
Parts of Kit Kat Fuse
- Fuse Base: It is made of porcelain or ceramic material. It provides a sturdy and insulated platform for mounting the fuse. It houses fixed terminals and contacts for electrical connections.
- Fuse Carrier: A removable unit that contains the fuse element. It is made of insulated material to ensure safety. It holds the arc resistance tube to extinguish arcs during operation.
- Fuse Element: The actual conducting element that melts when excessive current flows through the circuit. It is usually made of materials like copper, aluminum, or lead alloy.
- Fixed Contacts: Provides the electrical connection between the fuse carrier and the fixed terminals on the base.
- Arc Resistance Tube: A hollow or solid tube designed to contain and suppress the arc generated when the fuse blows.
- Cable Socket: A provision for connecting input and output cables securely to the fuse base.
Working of Kit Kat Fuse
When the circuit is operational under normal conditions, the fuse element allows the flow of current between the terminals. If an overcurrent or short-circuit fault occurs, the fuse element heats up and melts due to excessive current. This breaks the circuit, interrupting the flow of current and protecting the equipment. The arc resistance tube suppresses any arc generated during the fuse operation. The fuse carrier can be removed and replaced with a new fuse element for reuse.
Types of Kit Kat Fuses
| Type | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Single-Pole Kit Kat Fuse | Contains a single fuse element for single-phase circuits. | Domestic wiring, single-phase motors. |
| Double-Pole Kit Kat Fuse | Includes two fuse elements for both live and neutral protection. | Single-phase systems with neutral protection. |
| Triple-Pole Kit Kat Fuse | Designed with three fuse elements for three-phase circuits. | Three-phase motors, industrial machinery. |
| Four-Pole Kit Kat Fuse | For three-phase systems with a neutral connection. | Balanced industrial systems with neutral. |
| High-Current Kit Kat Fuse | Built for circuits with higher current ratings. | Industrial equipment with high loads. |
| Low-Voltage Kit Kat Fuse | Operates at lower voltages for small circuits. | Domestic applications, control panels. |
| Heavy-Duty Kit Kat Fuse | Reinforced design for demanding conditions. | Industrial setups, agricultural motors. |
Advantages of Kit Kat Fuse
- Simple and cost-effective design.
- Easy to install and replace.
- Durable porcelain construction for high thermal resistance.
- Reusable with a replaceable fuse element.
Disadvantages of Kit Kat Fuse
- Manual replacement of the fuse element is required after it blows.
- Provides no visual indication of the fault.
- Limited to low and medium-voltage applications.
Applications of Kit Kat Fuse
- Residential electrical systems for overcurrent protection.
- Industrial installations for controlling low-voltage circuits.
- Agricultural applications for motor and pump protection.
This type of fuse is popular for its simplicity and reliability in domestic and light industrial environments.
Key Characteristics of Kit Kat Fuse
- Voltage Range: Generally used in low and medium-voltage systems.
- Current Capacity: Available in various ratings, typically ranging from 16A to 200A or more.
- Material: Porcelain or ceramic base with a metallic fuse element.
- Ease of Use: Fuses are easy to replace by swapping the blown fuse element in the carrier.
Selection of Kit Kat Fuse
The choice of a Kit Kat fuse type depends on:
- Voltage and current rating of the circuit.
- Whether the application is single-phase or three-phase.
- Environmental factors such as temperature and load variation.
Related Posts
- HRC Fuse - Definition, Working, Diagram, Types & Applications
An HRC (High Rupturing Capacity) fuse is a type of fuse used in electrical systems…
- What is Servomotor? Working, Diagram, Types (AC & DC) & Applications
Servomotors are also known as "control motors". They are generally used in feedback control systems as…
- What is an Autotransformer? Working Principle, Construction, Types & Applications
Unlike two winding transformer, an auto-transformer contains only one winding. This single winding serves the…
- What is Megger? Working, Construction, Diagram & Applications
Megger is a portable instrument for measuring high resistances in which the voltage range can…
- What is Vapour Pressure Thermometer? Working, Construction, Diagram & Applications
In Vapour Pressure Thermometers, a filling substance may be liquid, gas or vapour. Vapour pressure…