A Gas Insulated Substation (GIS) is a high-voltage substation in which the primary components are enclosed in an insulating gas medium, typically sulfur hexafluoride (SF₆). GIS is known for its compact and enclosed design, which makes it suitable for urban or restricted spaces. Below, we explore its definition, construction, working, types, advantages, disadvantages, and applications.
What is Gas Insulated Substation?
A Gas Insulated Substation (GIS) is an advanced type of electrical substation where major electrical equipment, such as circuit breakers, bus bars, and disconnectors, are encapsulated in a metal enclosure filled with SF₆ gas. The gas acts as an insulating and arc-extinguishing medium.
Diagram Explanation
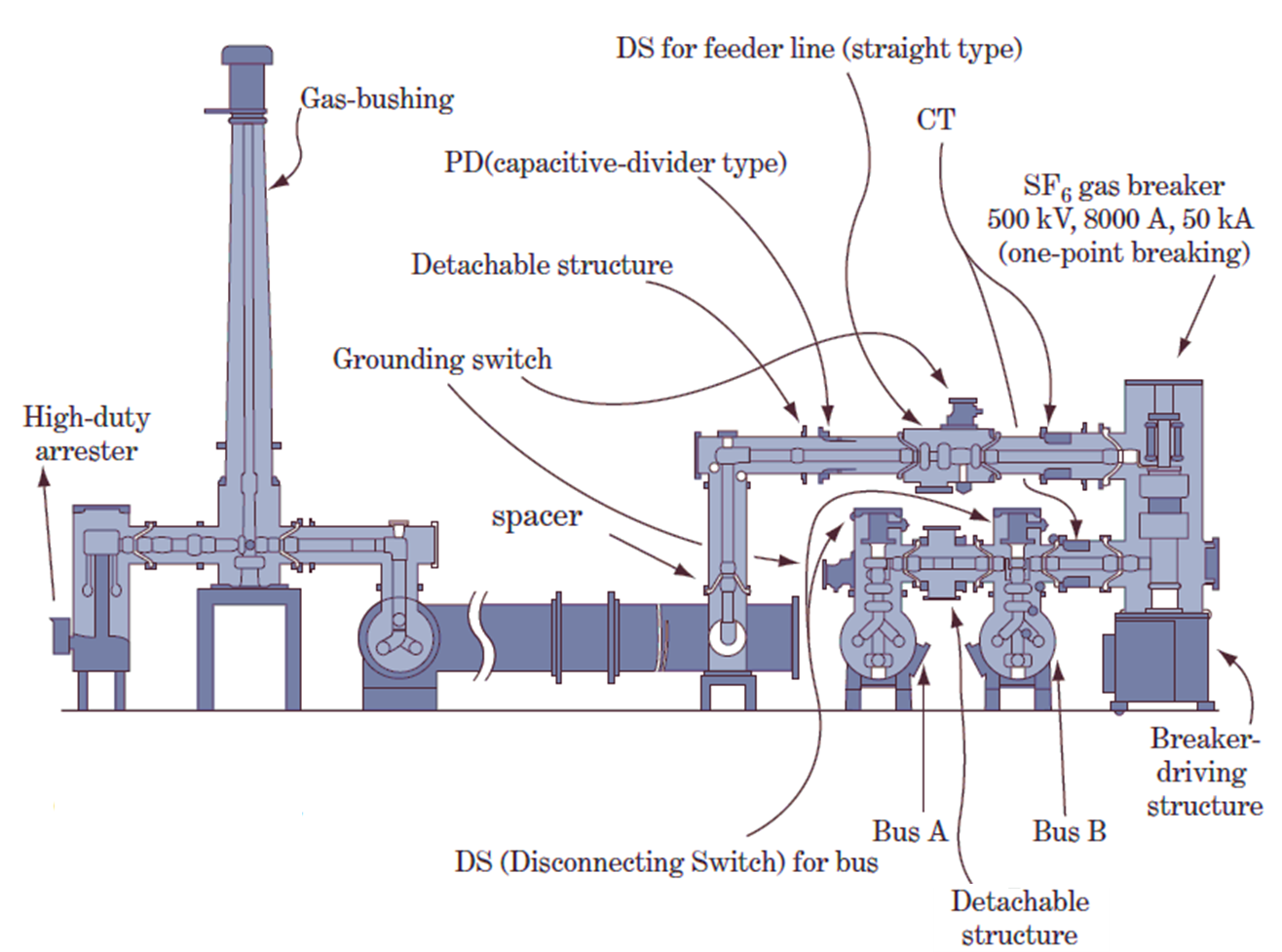
Figure 1.
The figure 1 illustrates a GIS system, highlighting components such as:
- Gas bushing for high-voltage connections.
- SF₆ gas breakers for circuit protection.
- Bus bars (Bus A and Bus B) for power transfer.
- Grounding switches, disconnectors, and high-duty arresters for enhanced functionality.
Construction of Gas Insulated Substation (GIS)
The main components of a GIS include:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| SF₆ Gas | Primary insulating medium with high dielectric strength and arc-quenching properties. |
| Gas Bushing | Connects the GIS to high-voltage lines, ensuring proper insulation and support. |
| Circuit Breaker | Encased in SF₆ gas for fault interruption and circuit protection. |
| Disconnector and Grounding Switch | Ensures safe isolation and grounding for maintenance operations. |
| Bus Bars | Conduct power between different GIS sections, insulated by SF₆ gas. |
| Current Transformer (CT) | Measures current for protection and metering purposes. |
| Voltage Transformer (VT) | Provides voltage measurement for control and monitoring. |
| Spacer | Maintains physical separation between GIS components. |
| High-Duty Arrester | Protects GIS components from lightning and switching surges. |
| Enclosures | Metal enclosures (aluminum or stainless steel) protect components and prevent gas leakage. |
Working of Gas Insulated Substation (GIS)
GIS operates on the same principle as a conventional substation but utilizes SF₆ gas for insulation and arc extinction. Key steps include:
- Insulation: SF₆ gas surrounds the live components, providing high dielectric strength and preventing electrical breakdown.
- Current Flow: Electrical power is transmitted through bus bars, switchgear, and transformers enclosed in the GIS.
- Fault Protection: Circuit breakers, protected by SF₆ gas, interrupt current flow during faults.
- Switching: Disconnectors isolate parts of the GIS, and grounding switches ensure maintenance safety.
Types of Gas Insulated Substation (GIS)
- Isolated Phase GIS: Each phase is enclosed in a separate compartment.
- Integrated 3-Phase GIS: All three phases share a single enclosure.
- Hybrid GIS: Combines air-insulated and gas-insulated technology.
- Compact GIS: Designed for limited spaces, with reduced dimensions.
Difference between Air Insulated Substation (AIS) and Gas Insulated Substation (GIS)
| Feature | Air Insulated Substation (AIS) | Gas Insulated Substation (GIS) |
|---|---|---|
| Insulation Medium | Uses air as the primary insulation medium. | Uses SF₆ gas as the primary insulation medium. |
| Space Requirement | Requires large space due to open-air design. | Compact design requires significantly less space. |
| Cost | Lower initial cost. | Higher initial cost due to equipment and gas handling. |
| Maintenance | Higher maintenance due to exposure to environmental factors. | Low maintenance due to enclosed design. |
| Reliability | Less reliable in extreme weather conditions. | Highly reliable in harsh environments. |
| Environmental Impact | No significant environmental concerns. | SF₆ gas is a potent greenhouse gas. |
| Application | Suitable for rural and less space-constrained areas. | Ideal for urban areas and space-constrained locations. |
Advantages of Gas Insulated Substation (GIS)
- Space-Saving Design: Ideal for urban areas and indoor installations.
- High Reliability: SF₆ insulation minimizes the risk of faults.
- Low Maintenance: Enclosed components reduce exposure to environmental conditions.
- Safety: Gas enclosure prevents electrical hazards.
- Environmental Resistance: Performs well in extreme weather conditions.
Disadvantages of Gas Insulated Substation (GIS)
- High Cost: Initial setup and SF₆ gas handling increase expenses.
- Environmental Concerns: SF₆ is a potent greenhouse gas.
- Complex Repairs: Specialized knowledge and equipment are needed.
- Gas Leakage Risks: Leaks can lead to system inefficiencies and safety issues.
Applications of Gas Insulated Substation (GIS)
- Urban Substations: Compact design suits dense city environments.
- Power Transmission: Efficient in transmitting high-voltage power over long distances.
- Industrial Facilities: Serves industries requiring high reliability.
- Renewable Energy: Integrates seamlessly with wind and solar farms.
- Critical Installations: Used in airports, railways, and data centers where downtime is not an option.