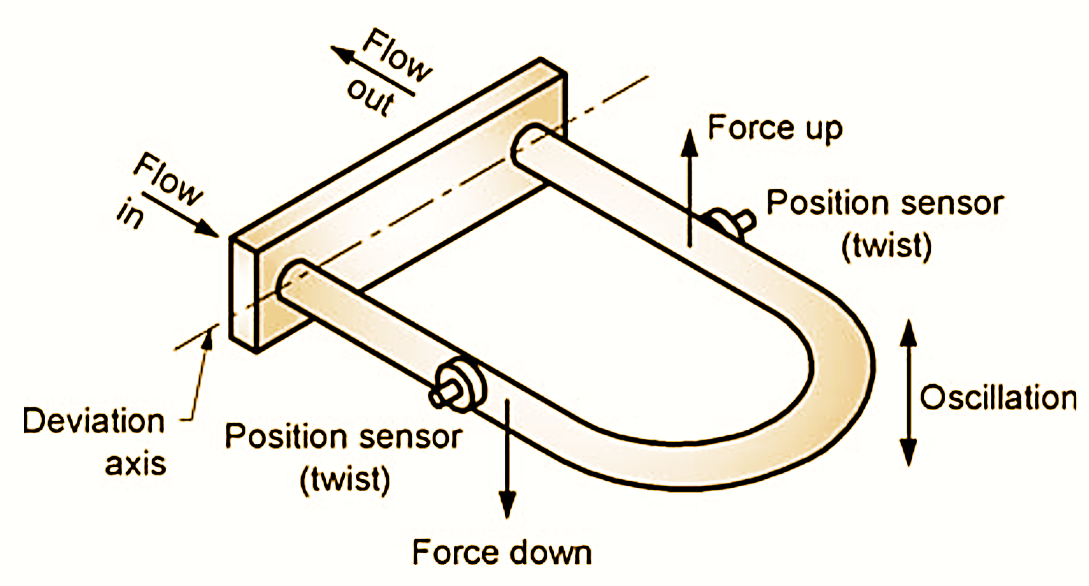
Figure 1: Coriolis Flow Meter.
The coriolis flowmeter is primarily used to measure the mass flow rate of liquids, and in some cases gas flow measurements. The construction of coriolis flow meter is shown in Fig. 1. It consists of either a pair of parallel vibrating tubes or else a single vibrating tube that is formed into a configuration that has two parallel sections.
Working Principle of Coriolis Flow Meter
A coriolis flowmeter requires force acting on a tube carrying a flowing fluid. This force actually deforms tubes through which the fluid flows. The amount of deformation depends directly on the mass flow rate through the tubes.
Construction and Working of Coriolis Flow Meter
Tubes are made of various materials of which stainless steel is the most common. They are available in different shapes such as B-shape, D-shape, U-shape etc. The Fig. 1 shows U-shape tube in more detail. The tubes are anchored at two points. The electromechanical drive unit between the two anchors excites vibrations in each tube at the tube resonant frequency.
In the tube, the fluid moves away from and back towards the axis of oscillation, resulting in a changing angular momentum of the fluid. The tube oscillation results into two opposite forces which twist the tube. First one way then the other with each oscillation cycle. The output from pickup sensors are sine waves showing oscillation frequency. Measuring the magnitude of deformation, the mass now rate can be measured.
Advantages of Coriolis Flow Meter
- Its measuring principle is independent of fluids pressure, density and viscosity.
- Its measurement is independent on Reynold’s number.
- Its measurement also independent on upstream and down stream flow velocities.
- The meter has high accuracy and high reliability.
Disadvantages of Coriolis Flow Meter
- Pipe line size is limited and available upto pipe size of 150 mm only.
- Initial cost is high